108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CEP55 通过 PI3K/Akt 途径促进食管鳞状细胞癌的增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Jia Y, Xiao Z, Gongsun X, Xin Z, Shang B, Chen G, Wang Z, Jiang W
Received 21 March 2018
Accepted for publication 7 June 2018
Published 20 July 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 4221—4232
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S168861
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
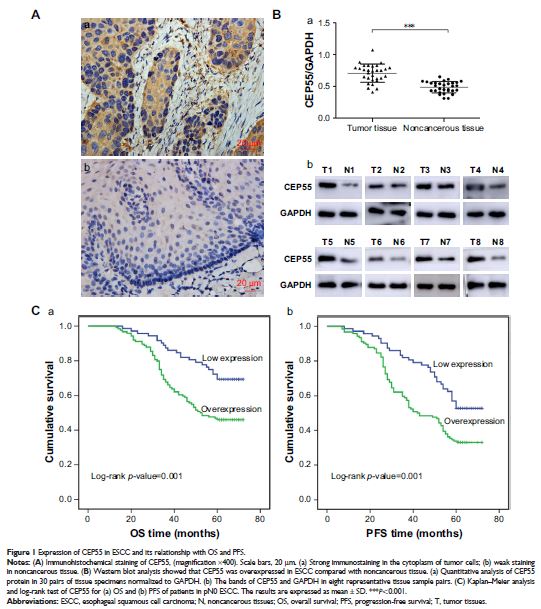
Background: Centrosomal
protein 55 (CEP55) is an important prognostic biomarker that plays an essential
role in the proliferation, migration and invasion of multiple tumors. We aimed
to investigate the prognostic value of CEP55 in pN0 esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma (ESCC) and explore its biological function in ESCC cells.
Methods: We used immunohistochemistry and Western blot analysis to detect
the expression of CEP55 in ESCC. Furthermore, both in vitro and in vivo assays
were used to determine the effect of CEP55 on malignant behavior in ESCC cells.
Results: As expected, we found that CEP55 was overexpressed in ESCC.
Univariate and multivariate analyses demonstrated that patients with CEP55
overexpression had a poor prognosis. Additionally, the abilities of
proliferation, migration and invasion of cells, as well as the
epithelial–mesenchymal transition markers, were all altered with the changed
CEP55 expression levels in ESCC cells. Further study elucidated that CEP55
facilitated ESCC via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Blockade of this pathway markedly
attenuated CEP55-mediated proliferation, migration, invasion and
epithelial–mesenchymal transition of ESCC cells.
Conclusion: Oncogenic CEP55 correlates with a poor prognosis by regulating
tumor cell proliferation, migration and invasion via the PI3K/Akt pathway. It
can serve as a promising prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target of pN0
ESCC after Ivor-Lewis esophagectomy.
Keywords: CEP55, proliferation, migration, invasion, esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma, PI3K/Akt pathway