108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

基质金属蛋白酶-7 可以作为宫颈癌的新型生物标志物
Authors Zhu L, Zheng X, Du Y, Xing Y, Xu K, Cui L
Received 31 December 2017
Accepted for publication 26 April 2018
Published 20 July 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 4207—4220
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S160998
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background: The
biological and clinical significance of matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7) in
cervical cancer remains unknown. Here, we investigated the function of MMP-7 in
cervical cancer cells and evaluated its clinical significance in both tissues
and serum from cervical cancer patients.
Methods: First, we analyzed the expression of MMP-7 in cervical cancer
using Oncomine microarray data and examined its expression in cervical tissues
by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting.
Second, we utilized gene silencing to explore the role of MMP-7 in cells.
Finally, we examined the MMP-7 levels in patients with cervical cancer and
normal serum by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Moreover, we further
investigated the relationship between MMP-7 expression and pathological
features.
Results: The mRNA and protein MMP-7 levels were higher in cervical cancer
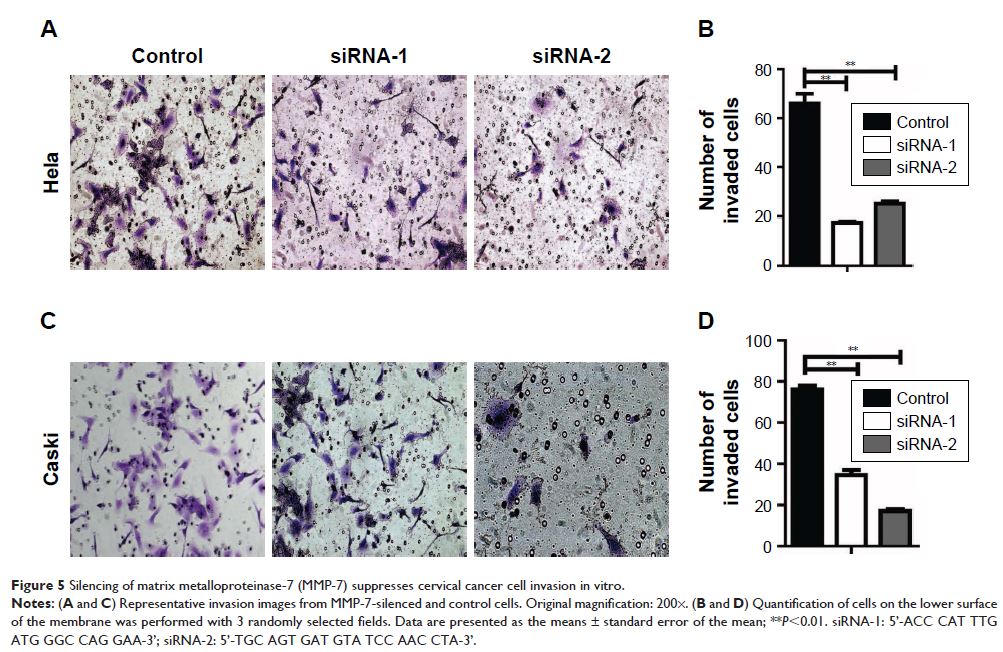
tissues than in healthy controls. Silencing of MMP-7 significantly decreased
cervical cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. The serum MMP-7
levels were significantly higher in cervical cancer patients than in healthy
subjects (P <0.01). Further, higher MMP-7
expression was associated with increased lymph metastasis (P =0.021), pathological grade (P =0.039, P=0.047), and clinical stage (P =0.049, P =0.046).
Conclusion: MMP-7 appears to act as an oncogene in cervical cancer cells and
is involved in cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. MMP-7 expression
was significantly higher in the tissue and serum of cervical cancer patients
compared to healthy individuals and was correlated with increased pathalogical
grade, clinical stage, and lymph metastasis. Therefore, our data provide novel
evidence that MMP-7 may be a clinically relevant biomarker for cervical cancer.
Keywords: cervical cancer, matrix metalloproteinase-7, biomarker, migration,
invasion