108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

微小 RNA-384 通过靶向 CDC42 抑制神经胶质瘤的增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Gu G, Wang L, Zhang J, Wang H, Tan T, Zhang G
Received 27 February 2018
Accepted for publication 18 April 2018
Published 16 July 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 4075—4085
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S166747
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Narasimha Reddy Parine
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
Background: Accumulative evidence indicated that microRNAs (miRNAs) play a critical
role in carcinogenesis and biological behaviors of glioma. Further
bio-molecular mechanisms of miRNAs in glioma cells remain largely unknown,
which can contribute to novel therapeutic strategy.
Methods: In the present study, we detected the expression level of miR-384 by
RT-PCR and Western blot. Meanwhile, Gain and loss function assay of miR-384 by
transfection of miR-384 mimics and inhibitor. Moreover, wild and mutant
psiCHECK-2-CDC42-3’-UTR luciferase reporter vectors were constructed and
transfected into glioma cells with miR-384 mimics or miR-NC.
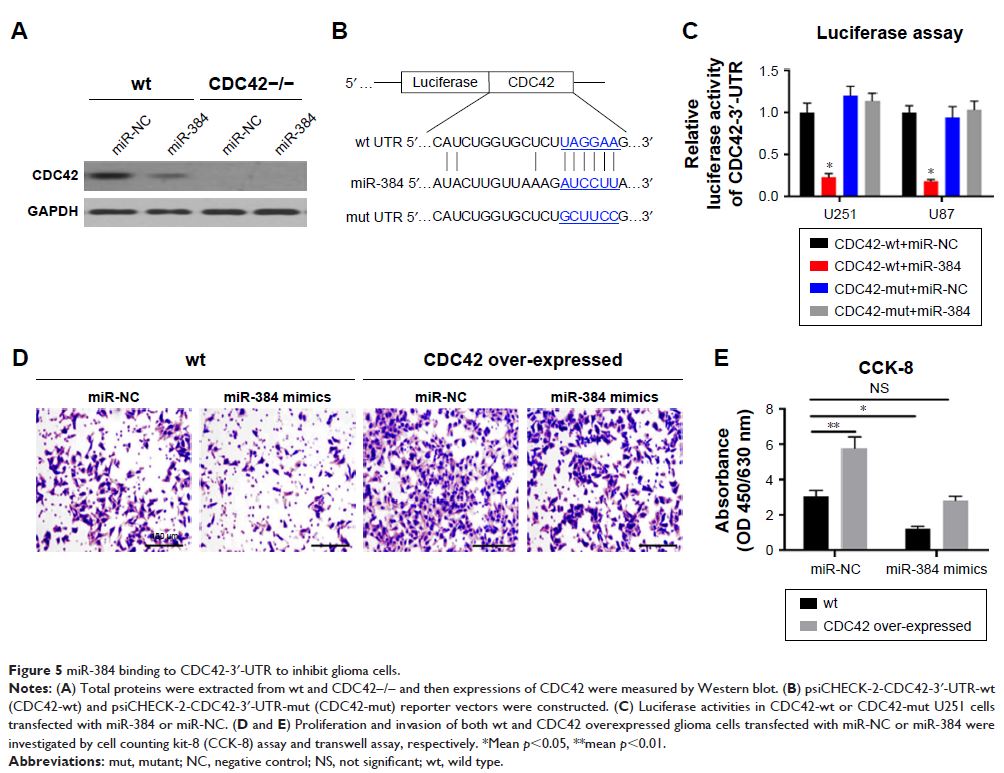
Results: miR-384 was dramatically down-regulated in human glioma tissues. It was
also demonstrated that miR-384 significantly inhibited proliferation, migration
and invasion of glioma cells. Cell division cycle 42 (Cdc42) was a direct
target of miR-384 according to results of RT-PCR and Western blotting.
Conclusion: Our research demonstrated that miR-384 exerted an inhibitory effect on
proliferation, migration and invasion of glioma via suppressing the expression
of CDC42 , meaning that miR-384 may be
regarded as a potential target in the treatment of glioma.
Keywords: miR-384, CDC42, glioma, proliferation, invasion