108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

用于口服递送白藜芦醇的半乳糖基化 PLGA 纳米颗粒:增强的生物利用度和体外抗炎活性
Authors Siu FYK, Ye S, Lin H, Li S
Received 31 January 2018
Accepted for publication 16 March 2018
Published 13 July 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 4133—4144
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S164235
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Resveratrol (RES) is a natural anti-inflammatory and antioxidant
compound with poor water solubility and oral bioavailability. The present study
takes the advantages of nanocarriers combined with a ligand (galactose)
anchoring to orally deliver RES in an attempt to improve its bioavailability
and pharmacological activity.
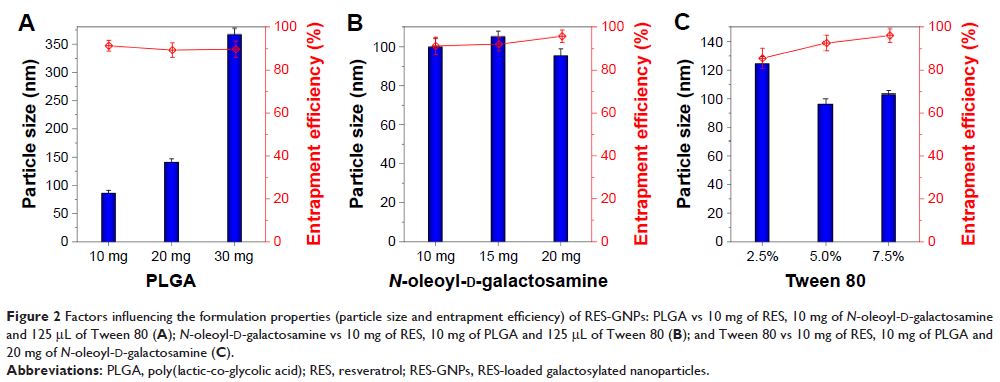
Methods: RES-loaded galactosylated nanoparticles (RES-GNPs) were prepared
by solvent diffusion technique using poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid),
synthesized N-oleoyl-d-galactosamine and Tween
80. RES-GNPs were characterized by particle size, morphology, entrapment
efficiency (EE) and in vitro release. Oral bioavailability and in vitro
anti-inflammatory activity were investigated in rats and lipopolysaccharides-induced
RAW 264.7 cells, respectively.
Results: The resulting RES-GNPs were 108.4 nm around in particle size with
a polydispersity index of 0.217. Furthermore, RES-GNPs possessed a high EE and
a slow drug release in water. After oral administration, RES-GNPs significantly
enhanced the oral bioavailability of RES, up to 335.7% relative to RES
suspensions. In situ single-pass intestinal perfusion and cellular uptake
experiments showed that GNPs could improve the intestinal permeability and
transcellular transport of RES. Moreover, the anti-inflammatory efficacy of
RES-GNPs in RAW 264.7 cells model was superior to free RES and RES-GNPs.
Conclusion: The results indicate that RES-GNPs can effectively promote the
intestinal absorption of RES and strengthen its bioactivity, which may be a
promising system for the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: resveratrol, polymeric nanoparticles, galactosylation, oral
bioavailability, anti-inflammation