108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

开发具有介孔结构的氧化锡载体,用于改善非诺贝特的溶出速率和口服相对生物利用度
Authors Bai A, Wu C, Liu X, Lv H, Xu X, Cao Y, Shang W, Hu L, Liu Y
Received 1 March 2018
Accepted for publication 1 May 2018
Published 10 July 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 2129—2138
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S166989
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
Background: Biopharmaceutics classification system class II drugs have low
solubility, which limits their extent and speed of absorption after oral
administration. Over the years, mesoporous materials have been widely used to
increase the dissolution rate and oral relative bioavailability of poorly
water-soluble drugs.
Objectives: In order to improve the dissolution rate and increase oral
relative bioavailability of the poorly water-soluble drugs, a tin oxide carrier
(MSn) with a mesoporous structure was successfully synthesized.
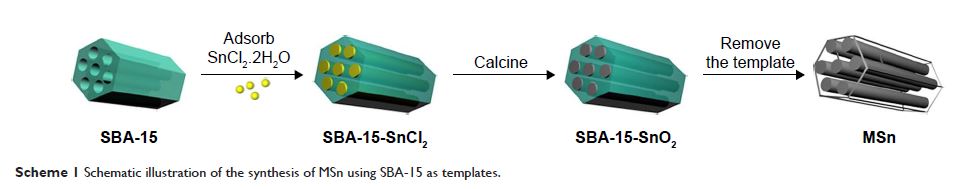
Methods: In this study, MSn was synthesized using mesoporous silica
material (SBA-15) as the template. Fenofibrate (FNB) was adsorbed into the
channels of MSn by an adsorption method. Characterizations of the pure FNB,
MSn, physical mixture of the drug and MSn (PM; 1:1) and FNB-loaded MSn
(FNB-MSn) samples were carried out by the scanning electron microscopy (SEM),
transmission electron microscopy (TEM), N2 adsorption/desorption, powder X-ray diffractometer (PXRD),
differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR)
spectroscopy. Cytotoxicity assay (MTT) was used to evaluate the cytotoxicity of
MSn. In vitro dissolution studies were performed to investigate the dissolution
rate of FNB-MSn. In vivo pharmacokinetic studies were used to investigate the
changes of plasma drug concentrations of FNB-MSn tablets and commercial FNB
tablets in rabbits.
Results: Detailed characterization showed that FNB in the channels of MSn
was present in an amorphous state. The in vitro release tests demonstrated that
MSn with a good biocompatibility could effectively enhance the dissolution rate
of FNB. Pharmacokinetic results indicated that MSn significantly increased the
oral relative bioavailability of FNB.
Conclusion: MSn can be regarded as a promising carrier for an oral drug
delivery system.
Keywords: tin oxide, mesoporous material, fenofibrate, dissolution rate,
oral relative bioavailability