108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

土贝母苷甲 -1 对口腔鳞状细胞癌增殖、转移和凋亡的体外疗效
Authors Wu T, Cui H, Xu Y, Du Q, Zhao E, Cao J, Nie L, Fu G, Ren A
Received 3 February 2018
Accepted for publication 25 April 2018
Published 10 July 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 3989—4000
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S164503
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
Background: Tubeimoside-1 (TBMS1), a triterpenoid saponin extracted from traditional
Chinese medicine tubeimoside, exerts a cytotoxic effect on several human cancer
cell lines. However, no study has focused on whether TBMS1 works on oral
squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC).
Materials and
methods: We treated OSCC cells with TBMS1
to detect the effect and relevant molecular basis of TBMS1 for the first time.
We chose two oral cancer cell lines, CAL27 and SCC15, for this study. First,
the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenylte-trazolium bromide assay and
cell proliferation 5'-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine assay were carried out to
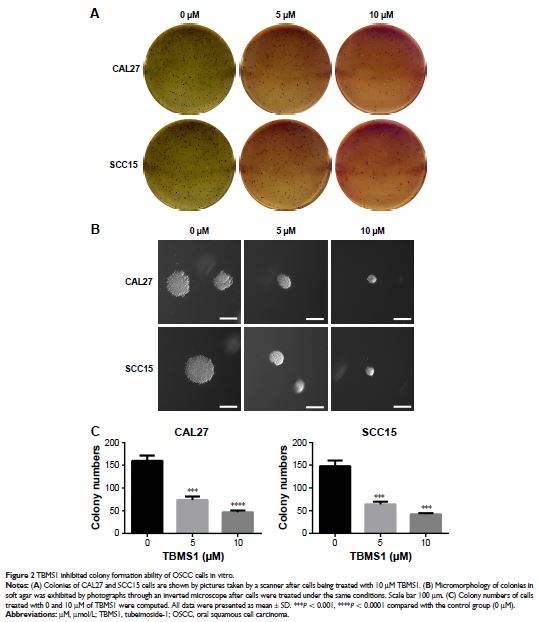
detect cell growth. Second, colony formation assay was performed to assess
clonogenesis capacity. Next apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometry.
Subsequently, wound healing and transwell assays were applied to explore cell
migration. Finally, Western blot was further performed to examine corresponding
proteins’ expression change.
Results: Our data showed that TBMS1 significantly suppressed proliferation
of OSCC cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner and it inhibited migration
of OSCC cells as well. After treatment with TBMS1, OSCC cells underwent cell
apoptosis. Furthermore, Western blot demonstrated that TBMS1 downregulated
apoptosis-associated proteins such as PARP, p-ERK1/2, Bcl-2, caspase-3,
caspase-7 and caspase-8 and upregulated cleaved PARP, cleaved caspase-3 and
cleaved caspase-9. It could also reduce expression of c-Myc and MMP-7.
Meanwhile, TBMS1 did not change the total ERK1/2 expression.
Conclusion: These results revealed that TBMS1 might be a potential
chemotherapeutic drug for the management of OSCC.
Keywords: tubeimoside-1, chemotherapeutic drug, oral squamous cell
carcinoma, OSCC, apoptosis, underlying mechanism