108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过阻断己糖激酶-2 磷酸化,柠檬苦素抑制肿瘤糖酵解并诱导肝细胞癌细胞凋亡
Authors Yao J, Liu J, Zhao W
Received 10 February 2018
Accepted for publication 20 April 2018
Published 3 July 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 3793—3803
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S165220
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Introduction: The purpose of present study was to investigate the effect of
limonin on tumor glycolysis and the underlying mechanisms in hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC).
Methods: Cell proliferation and colony formation assays were performed to
evaluate the potency of limonin against HCC cells in vitro. The glucose
consumption and lactate production after limonin treatment was determined. The
effect of limonin on hexokinase-2 ( HK-2) activity was assessed and the
mitochondrial location of HK-2 was studied by immunoprecipitation. Cell
apoptosis and protein expression were detected by flow cytometry and western
blotting respectively. Protein overexpression by plasmid transfection was
adopted to investigate the molecular mechanisms.
Results: HCC proliferation and colony formation were inhibited by limonin
in vitro. With the suppression of HK-2 activity, the glycolytic level in HCC
cells was substantially reduced, which was evidenced by the decrease of glucose
consumption and lactate production. The phosphorylation of HK-2 was
substantially inhibited by limonin, which resulted in the disassociation of
HK-2 from mitochondria. Due to the reduction of HK-2 in mitochondria,
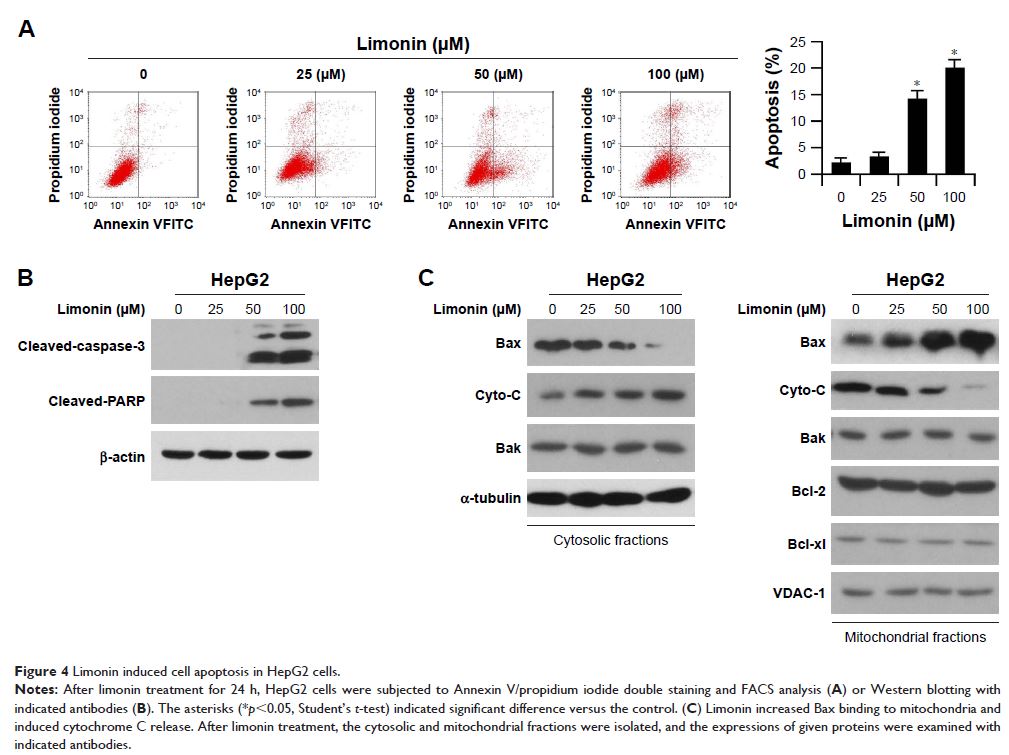
increasing Bax were shifted to the mitochondria and gave rise to the release of
cytochrome C, which induced HCC cells to subject to mitochondria-mediated
apoptosis. Mechanism investigations revealed that the decrease of HK-2
phosphorylation was mainly due to the inhibition of Akt activity. In Akt
exogenously overexpressed HCC cells, limonin-mediated cell proliferation
inhibition, glycolysis suppression and apoptosis induction were significantly
impaired.
Conclusion: Limonin inhibited the tumor glycolysis in hepatocellular carcinoma
by suppressing HK-2 activity, and the suppression of HK-2 was closely related
to the decrease of Akt activity.
Keywords: apoptosis, limonin, tumor glycolysis, hexokinase-2