108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

lncRNA OGFRP1 下调通过 AKT/mTOR and Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路抑制肝细胞癌的进展
Authors Chen W, You J, Zheng Q, Zhu Y
Received 9 February 2018
Accepted for publication 13 April 2018
Published 2 July 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 1817—1826
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S164911
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Introduction: Increasing evidence demonstrates that long noncoding RNAs
(lncRNAs) play important roles in the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
(HCC) by regulating gene expression. However, the identification of functional
lncRNAs in HCC remains insufficient. Our study aimed to investigate the
function of lncRNA OGFRP1, which has not been functionally researched before,
in Hep3B and HepG2 cells.
Methods: lncRNA OGFRP1 in HCC cells was down-regulated by using RNAi
technology. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was used to
determine the mRNA expression of lncRNA OGFRP1. Cell proliferation was examined
by CCK8 and clone formation assays. Cell cycle and apoptosis were analyzed by
flow cytometry. Cell migration and invasion were assessed by using Scratch
assay and transwell assay, respectively. Protein expression of signaling
pathways was determined by using Western blot.
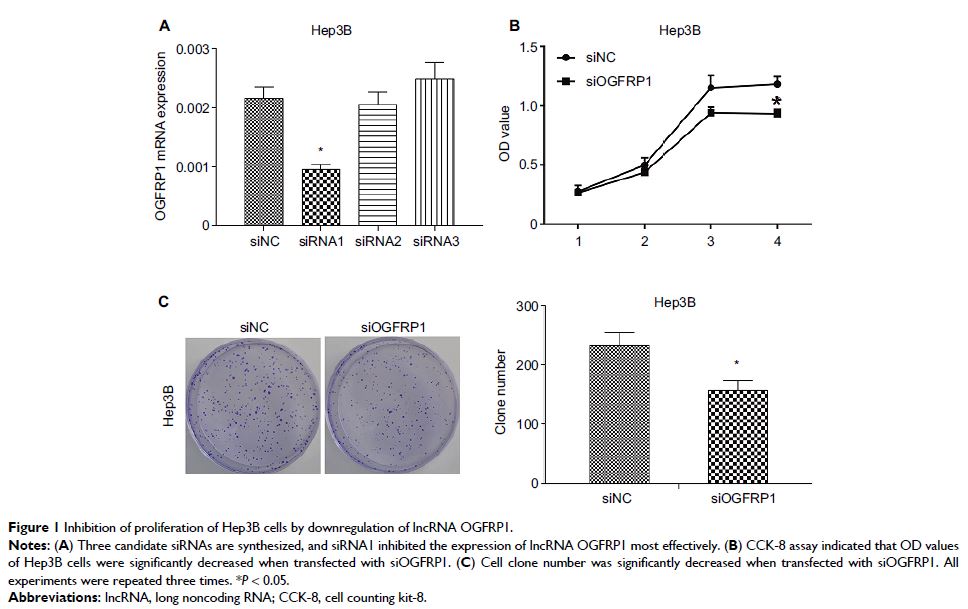
Results: Cell proliferation of Hep3B was significantly inhibited by
down-regulation of lncRNA OGFRP1 (P <0.05).
Moreover, siOGFRP1 transfection induced Hep3B cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
by regulating the expression of related proteins. Cell migration and invasion
of Hep3B were also significantly inhibited by down-regulation of lncRNA OGFRP1.
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, involved in epithelial–mesenchymal transition
(EMT), was inactivated by lncRNA OGFRP1 downregulation, including decreased
expression of Wnt3a, β-catenin, N-cadherin and vimentin and increased
expression of E-cadherin. We also found that the inhibitory effect of lncRNA
OGFRP1 knockdown on Hep3B was mediated by the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and
IGF-1, an AKT signaling activator, could rescue the cellular phenotype.
However, knockdown of lncRNA OGFRP1 did not influence cell proliferation,
migration and invasion in HepG2 cells.
Conclusion: We found that downregulation of lncRNA OGFRP1 suppressed the
proliferation and EMT of HCC Hep3B cells through AKT and Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathways. However, lncRNA OGFRP1 exhibited a differentiated function
in different HCC cell lines, which required further study in the future.
Keywords: lncRNA OGFRP1, HCC, EMT, AKT/mTOR, Wnt/β-catenin