108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

抑郁样行为大鼠电惊厥休克诱导的学习和记忆障碍与突触可塑性的变化有关
Authors Chen Q, Ren L, Min S, Hao X, Chen H, Deng J
Received 25 January 2018
Accepted for publication 28 March 2018
Published 2 July 2018 Volume 2018:14 Pages 1737—1746
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S163756
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Professor Wai Kwong Tang
Background: Accompanied with the effective antidepressant effect,
electroconvulsive shock (ECS) can induce cognitive impairment, but the
mechanism is unclear. Synaptic plasticity is the fundamental mechanism of
learning and memory. This study aimed to investigate the effect of ECS on
synaptic plasticity changes in rats with depression-like behavior.
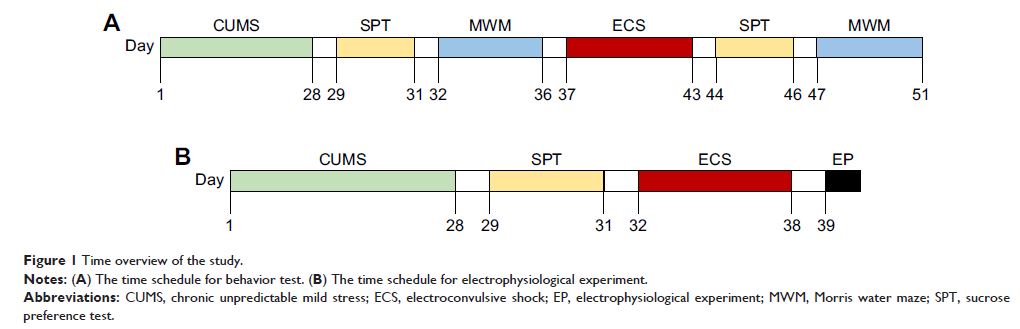
Methods: Chronic unpredictable mild stress procedure was conducted to
establish a model of depression-like behavior. Rats were randomly divided into
the following three groups: control group with healthy rats (group C), rats
with depression-like behavior (group D), and rats with depression-like behavior
undergoing ECS (group DE). Depression-like behavior and spatial learning and
memory function were assessed by sucrose preference test and Morris water test,
respectively. Synaptic plasticity changes in long-term potentiation (LTP),
long-term depression (LTD), depotentiation, and post-tetanic potentiation (PTP)
were tested by electrophysiological experiment.
Results: ECS could exert antidepressant effect and also induced spatial
learning and memory impairment in rats with depression-like behavior. And, data
on electrophysiological experiment showed that ECS induced lower magnitude of
LTP, higher magnitude of LTD, higher magnitude of depotentiation, and lower
magnitude of PTP.
Conclusion: ECS-induced learning and memory impairment may be attributed to
postsynaptic mechanism of LTP impairment, LTD and depotentiation enhancement,
and presynaptic mechanism of PTP impairment.
Keywords: electroconvulsive therapy, learning, memory, synaptic plasticity,
electrophysiology