108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

8-Br-cAMP 通过激活结直肠癌中 cAMP/PKA 途径抑制血管生成和血管生成拟态
Authors Wang S, Zhang Z, Qian W, Ji D, Wang Q, Ji B, Zhang Y, Zhang C, Sun Y, Zhu C, Sun Y
Received 8 February 2018
Accepted for publication 25 April 2018
Published 2 July 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 3765—3774
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S164982
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos E Vigil
Introduction: Vasculogenic mimicry (VM) describes the formation of an
epithelial-independent tumor microcirculation system that differs from
traditional angiogenesis. Angiogenesis and the formation of VM are closely
related through the cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)/protein kinase A
(PKA) pathway and the epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) process.
Materials and
methods: In this study, 8-Br-cAMP, a cAMP
analog and PKA activator, was used to activate the cAMP/PKA pathway to evaluate
the effects of cAMP/PKA on angiogenesis and VM in colorectal cancer (CRC)
cells. We used a syngeneic model of CRC in BALB/c mice.
Results: We discovered that treatment with 8-Br-cAMP significantly reduced
tumor number compared to control mice after the 7th, 14th, and 28th days of
treatment. VM was evaluated by periodic acid–schiff (PAS)–CD31 staining, and we
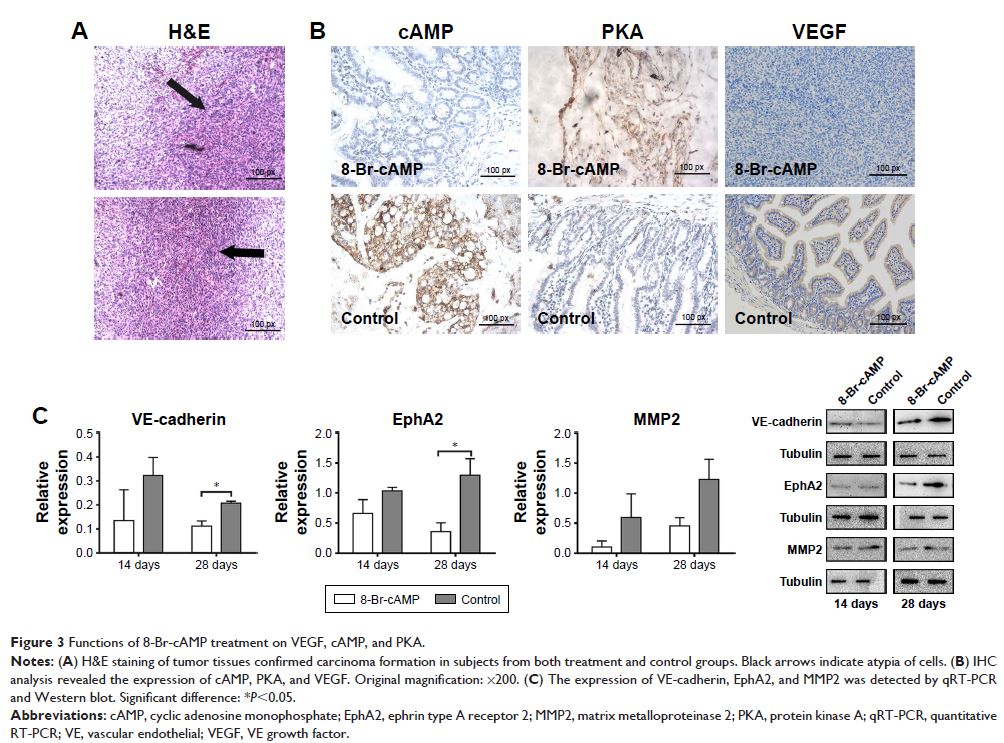
found that VM was inhibited by 8-Br-cAMP treatment in vivo. Immunohistochemistry
confirmed the inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and cAMP
and the activation of PKA by 8-Br-cAMP; quantitative real-time-PCR (qRT-PCR)
demonstrated that 8-Br-cAMP regulated the expression of vascular endothelial
(VE)-cadherin, matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2), ephrin type-A receptor 2
(EphA2), and VEGF in vivo. Experiments in vitro revealed that treatment with
8-Br-cAMP and U0126 decreased VEGF expression through PKA–ERK in CT26 cells by
qRT-PCR. We further confirmed that tube formation of human umbilical vein
endothelial cells was inhibited by 8-Br-cAMP in vitro.
Discussion: This study demonstrates that angiogenesis and VM are inhibited by
8-Br-cAMP treatment. Our data indicate that 8-Br-cAMP acts through the
cAMP/PKA–ERK pathway and through EMT processes in CRC. These findings provide
an insight into mechanisms of CRC and suggest that the cAMP/PKA–ERK pathway is
a novel potential therapeutic target for the treatment of CRC.
Keywords: vasculogenic mimicry, angiogenesis, VEGF, 8-Br-cAMP, cAMP