108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

包含 PD-1、IL-2Rα、IL-10 和 CA15-3 在内的小组,作为区分乳腺癌和良性乳腺疾病的生物标志物
Authors Liu C, Sun B, Xu B, Meng X, Li L, Cong Y, Liu J, Wang Q, Xuan L, Song Q, Wu S
Received 21 December 2017
Accepted for publication 16 April 2018
Published 26 June 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 1749—1761
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S160452
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Kenan Onel
Introduction: Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1), an immune checkpoint
molecule, has recently been recognized as a predictive and prognostic biomarker
in several malignant tumors, but its diagnostic value remains largely unknown.
We aimed to investigate the differential diagnostic efficiency of PD-1 and
other immune molecules and propose a panel of immune molecules combined with
cancer antigen 15-3 (CA15-3) to distinguish breast cancer (BC) from benign
breast disease (BBD).
Patients and
methods: Ninety-one eligible BC patients and
31 BBD patients were enrolled. Pretreatment peripheral blood was collected and
tested for mRNA expression of PD-1, cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4, forkhead
box P3, transforming growth factor beta, interleukin-10 (IL-10), IL-2 receptor
alpha (IL-2Rα), and cluster of differentiation 28 by quantitative reverse transcription
PCR.
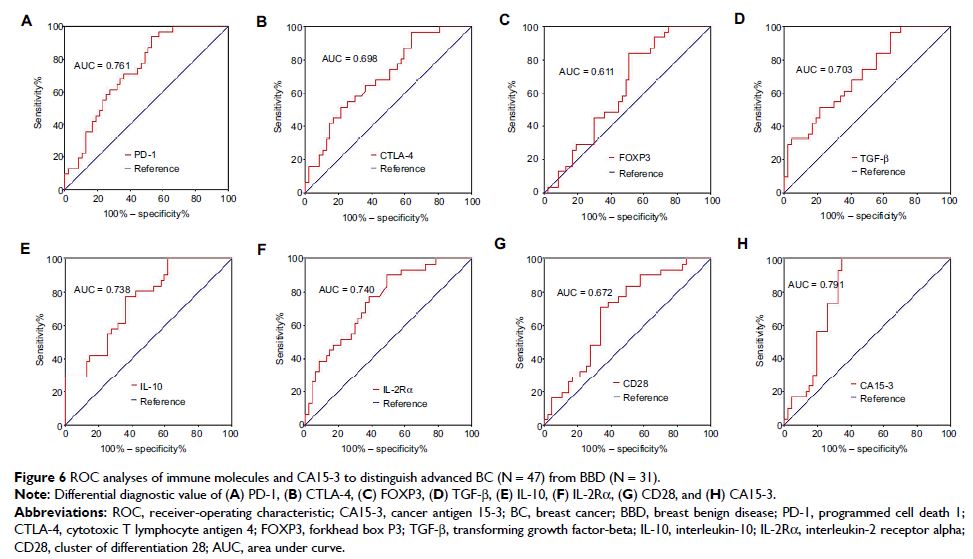
Results: The diagnostic areas under curve (AUCs) of PD-1, IL-2Rα, and IL-10
for BC–BBD discrimination were 0.764, 0.758, and 0.743, respectively. The
diagnostic efficiencies of these three parameters in distinguishing early-stage
or advanced BC from BBD were consistent with a role in BC–BBD discrimination. A
panel of PD-1 + IL-10 + IL-2Rα + CA15-3 showed the highest AUC (0.862), with a
sensitivity of 0.933 and a specificity of 0.724, for BC–BBD discrimination. In
addition, for early-stage BC discrimination, this panel also had the highest
AUC (0.811), with a sensitivity of 0.933 and a specificity of 0.614, while for
advanced BC discrimination, a panel of PD-1 + IL-10 + CA15-3 exhibited the
highest AUC (0.896), with a sensitivity of 0.933 and a specificity of 0.783.
Conclusion: These data indicate that the panel containing PD-1, IL-2Rα, IL-10,
and CA15-3 can effectively discriminate BC from BBD with a high efficiency.
After further confirmation, it could be used to complement conventional imaging
modalities, especially in discriminating early-stage BC from BBD.
Keywords: breast cancer, immune checkpoint, PD-1, CTLA-4, IL-2Rα, diagnosis,
biomarker