108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

洋川芎内酯 A 通过调节蛋白磷酸酶 2A 和 α-突触核蛋白信号传导保护神经细胞免于遭受皮质酮诱导的细胞凋亡
Authors Gong S, Zhang J, Guo Z, Fu W
Received 6 January 2018
Accepted for publication 12 April 2018
Published 25 June 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 1865—1879
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S161748
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Palas Chanda
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sukesh Voruganti
Background: Depression is characterized by a pathological injury to the
hippocampal neurons. Senkyunolide A (SenA) is one of the major active
components of Dan-zhi-xiao-yao-san, which is widely used in the treatment of
depression-related disorders.
Materials and
methods: In the present study, it was
hypothesized that the antidepressant effect of Dan-zhi-xiao-yao-san depended on
the function of SenA and the authors attempted to reveal the molecular
mechanism associated with the treatment. An in vitro depression model was
induced using corticosterone (Cort), and the effect of SenA on the cell
viability, apoptosis, and protein phosphatase 2A/α-synuclein (PP2A/α-syn)
signaling was detected. To validate the mechanism driving the therapeutic
effect of SenA, activity of PP2A and α-syn was modulated and the effect on
neural cells was evaluated.
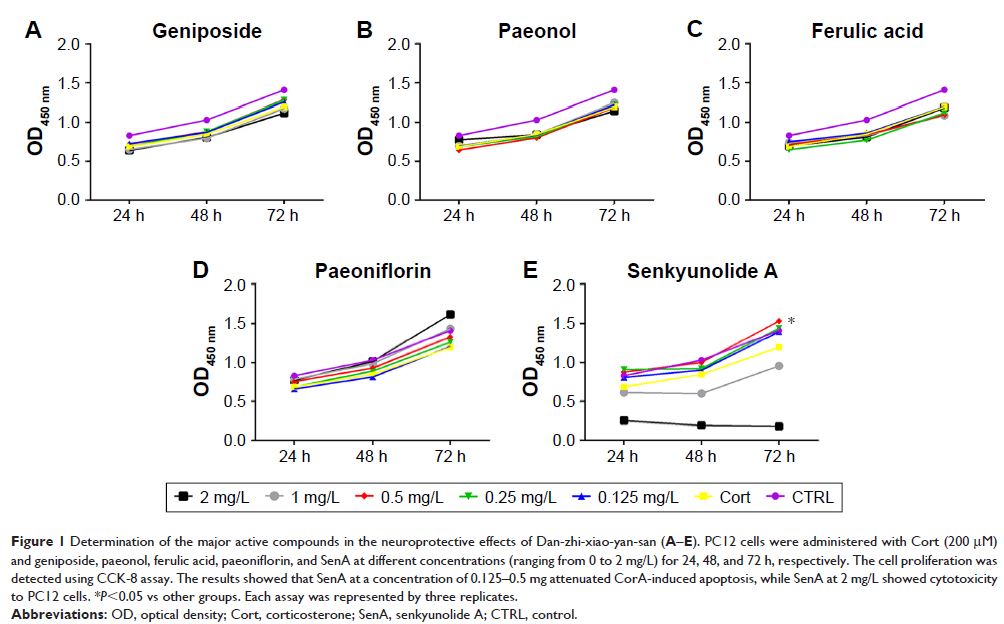
Results: The results showed that SenA protects Cort-induced cell apoptosis
in PC12 cells. In addition, SenA increased Cort-induced reduction of PP2A
activity, while it decreased the expression of p-PP2A, α-syn, and p-α-syn
(Ser129). Further, modulation of PP2A activity with specific inhibitor okadaic
acid (OA) increased Cort-induced cell apoptosis, while PP2A activator
D-erythro-sphingosine (SPH) exhibited an opposite effect. The neuroprotective
effects of SenA on neural cells also depended on inhibition of α-syn function,
the regulation of which would influence the activity of PP2A in a negative
loop.
Conclusion: Collectively, the results suggested that the neuroprotective effects of
SenA were exerted by modulating activities of PP2A activities and α-syn. The
findings partially explained the mechanism associated with the neuroprotective
effect of SenA.
Keywords: α-synuclein, corticosterone, depression, neuroprotection, protein phosphatase
2A, senkyunolide A