109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
具有中孔大小和孔隙体积的介孔钙硅凝胶通过加载和持续释放 rhBMP-2 而对 hMSC 的行为产生影响
Authors Song W, Li X, Qian J, Lv G, Yan Y, Su J, Wei J
Published Date March 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 1715—1726
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S70934
Received 10 July 2014, Accepted 27 August 2014, Published 4 March 2015
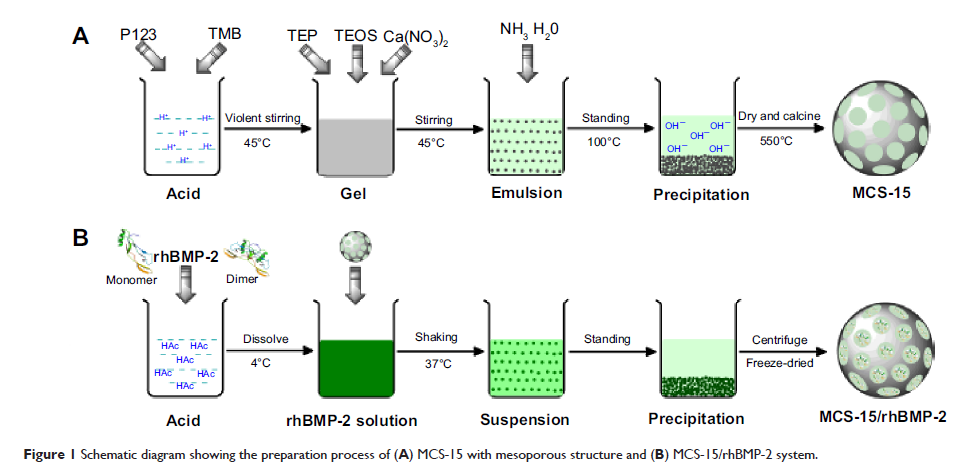
Abstract: Mesoporous calcium–silicon xerogels with a pore size of 15 nm (MCS-15)
and pore volume of 1.43 cm3/g were synthesized by using
1,3,5-mesitylene (TMB) as the pore-expanding agent. The MCS-15 exhibited good
degradability with the weight loss of 50 wt% after soaking in Tris-HCl solution
for 56 days, which was higher than the 30 wt% loss shown by mesoporous
calcium–silicon xerogels with a pore size of 4 nm (MCS-4). The pore size and
pore volume of MCS-15 had significant influences on load and release of
recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2). The MCS-15 had a
higher capacity to encapsulate a large amount of rhBMP-2; it could adsorb 45
mg/g of rhBMP-2 in phosphate-buffered saline after 24 hours, which was more
than twice that with MCS-4 (20 mg/g). Moreover, the MCS-15 system exhibited
sustained release of rhBMP-2 as compared with MCS-4 system (showing a burst
release). The MCS-15/rhBMP-2 system could promote the proliferation and
differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells, showing good cytocompatibility
and bioactivity. The results indicated that MCS-15, with larger mesopore size
and higher pore volume, might be a promising carrier for loading and sustained
release of rhBMP-2, which could be used as bone repair material with built-in
osteoinduction function in bone reconstruction.
Keywords: mesoporous calcium–silicon xerogels, pore size, pore volume, load-release, rhBMP-2