108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

现代放射治疗工作流程中的癌症风险评估与医学大数据
Authors Jin F, Luo HL, Zhou J, He YN, Liu XF, Zhong MS, Yang H, Li C, Li QC, Huang X, Tian XM, Qiu D, He GL, Yin L, Wang Y
Received 8 February 2018
Accepted for publication 4 May 2018
Published 22 June 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 1665—1675
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S164980
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leylah Drusbosky
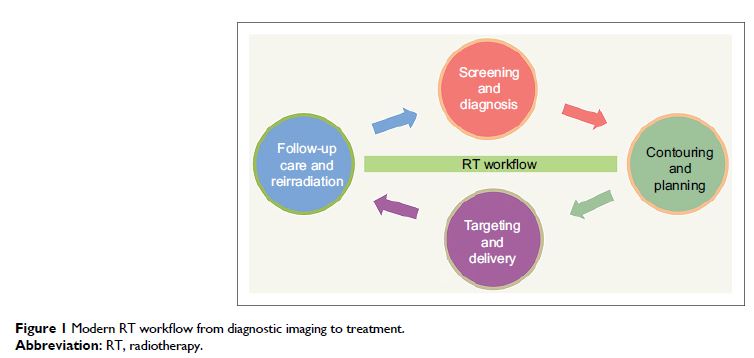
Abstract: Modern radiotherapy (RT) is being enriched by big digital data and
intensive technology. Multimodality image registration, intelligence-guided
planning, real-time tracking, image-guided RT (IGRT), and automatic follow-up
surveys are the products of the digital era. Enormous digital data are created
in the process of treatment, including benefits and risks. Generally, decision
making in RT tries to balance these two aspects, which is based on the archival
and retrieving of data from various platforms. However, modern risk-based
analysis shows that many errors that occur in radiation oncology are due to
failures in workflow. These errors can lead to imbalance between benefits and
risks. In addition, the exact mechanism and dose–response relationship for
radiation-induced malignancy are not well understood. The cancer risk in modern
RT workflow continues to be a problem. Therefore, in this review, we develop
risk assessments based on our current knowledge of IGRT and provide strategies
for cancer risk reduction. Artificial intelligence (AI) such as machine
learning is also discussed because big data are transforming RT via AI.
Keywords: cancer risk,
radiotherapy, workflow, big data