108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

TRPV1 在肾细胞癌中的表达下降:与肿瘤 Fuhrman 分级和组织病理学亚型相关
Authors Wu YY, Liu XY, Zhuo DX, Huang HB, Zhang FB, Liao SF
Received 24 February 2018
Accepted for publication 20 April 2018
Published 22 June 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 1647—1655
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S166390
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leylah Drusbosky
Purpose: The
aim of this study was to investigate whether the expression of the ligand-gated
Ca2+channel transient
receptor potential vanilloid type-1 (TRPV1) in primary human renal cell
carcinoma (RCC) is associated with clinicopathological features.
Patients and
methods: Fresh and frozen primary tumor and
normal peritumoral kidney tissues from 127 patients diagnosed with RCC were
analyzed for TRPV1 expression by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase
chain reaction (RT-PCR), Western blotting and immunohistochemistry.
Results: Quantitative RT-PCR revealed that TRPV1 was decreased 3.20-fold in RCC
tissue vs normal peritumoral kidney tissue (p =0.012).
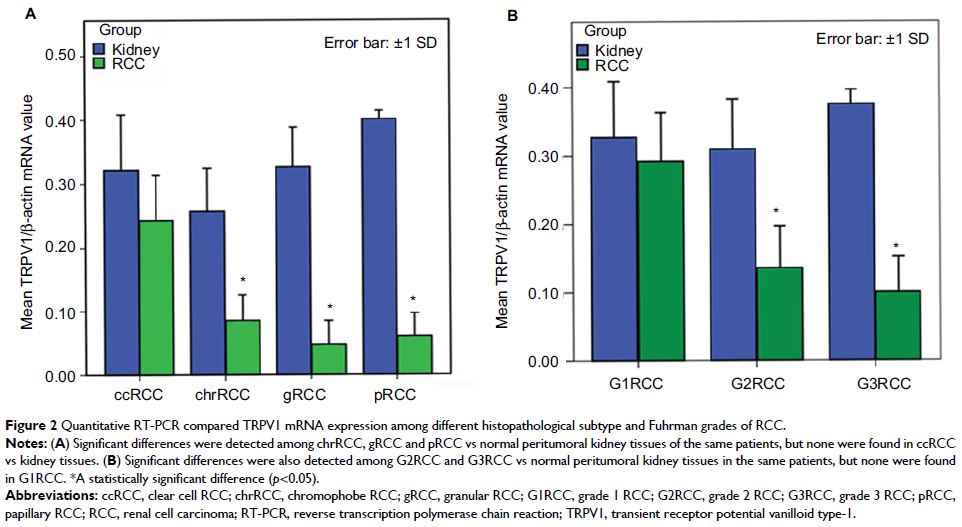
Significantly different TRPV1 mRNA expression was detected in RCC tissues of
different Fuhrman grades and histopathological subtypes (F=4.282, p =0.015 and F=5.205, p =0.014, respectively). Decreased
TRPV1 expression was correlated with RCC histopathological subtype
(R=-0.554, p =0.003) and Fuhrman grade
(R=−0.525, p =0.006). Western blot analysis of
TRPV1 protein expression showed similar results. Immunohistochemical analysis
showed strong expression of TRPV1 in kidney tubules but demonstrated weak or no
immunostaining in RCC tissues.
Conclusion: TRPV1 expression was decreased in RCC, which was significantly
associated with tumor Fuhrman grades and histopathological subtypes. It seems
to suggest that TRPV1 expression may be a valuable tool to predict the extent
of RCC progression.
Keywords: renal cell carcinoma, TRPV1, Fuhrman grade, histopathological
subtype, prognostic factor