108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

氧化锌纳米颗粒通过激活 PINK1/Parkin 介导的线粒体自噬可在 CAL 27 口腔癌细胞系中诱导毒性
Authors Wang J, Gao S, Wang S, Xu Z, Wei L
Received 16 February 2018
Accepted for publication 26 April 2018
Published 20 June 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 3441—3450
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S165699
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Tongue squamous cell carcinoma (tongue cancer) is one of the most common
malignancies in the oral maxillofacial region. The tumor easily relapses after
surgery, and the prognosis remains poor. Recently, zinc oxide nanoparticles
(ZnO NPs) were shown to target multiple cancer cell types. In this study, we
aimed to elucidate the anticancer effect of ZnO NPs on CAL 27 human tongue
cancer cells and identify the role of PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy in this
effect.
Materials and
methods: We analyzed the dose-dependent
cytotoxic effects of ZnO NPs on CAL 27 cells. Cells were cultured in media
containing 0, 5, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, or 100 µg/mL ZnO NPs for
24 h. We further examined the intracellular reactive oxygen species levels,
monodansylcadaverine intensity and mitochondrial membrane potential following
the administration of 25 µg/mL ZnO NPs for 4, 8, 12, or 24 h and investigated
the role of PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy in ZnO NP-induced toxicity in CAL
27 cells.
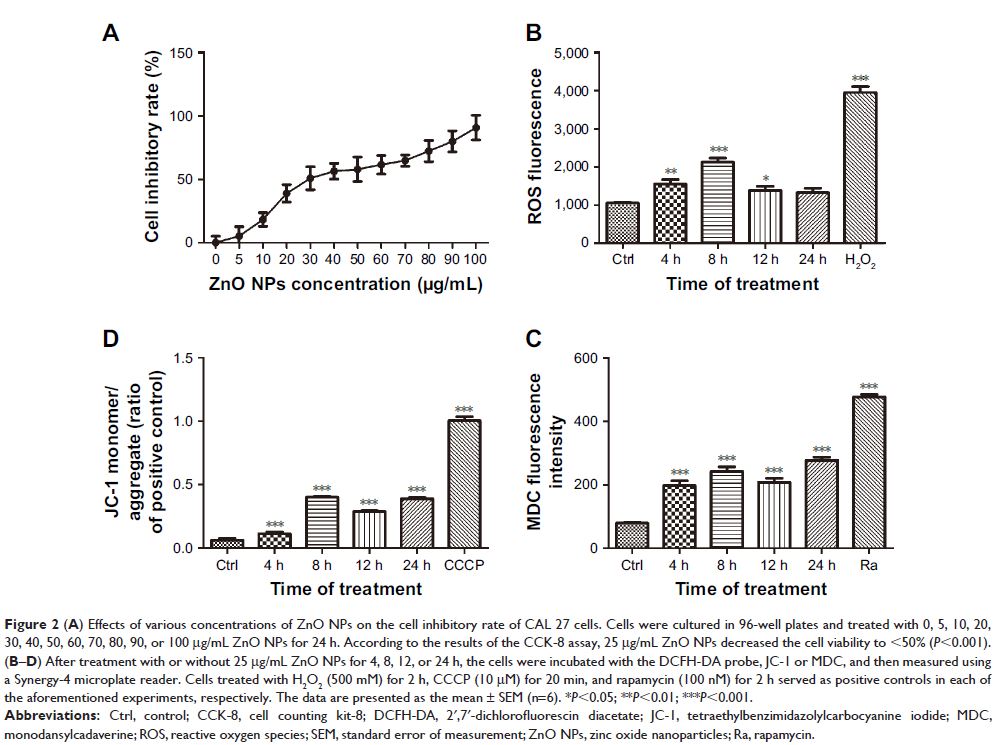
Results: The viability of CAL 27 cells decreased after treatment with
increasing ZnO NP concentrations. The inhibitory concentration 50% of the ZnO
NPs was calculated as 25 µg/mL. The ZnO NPs increased the intracellular
reactive oxygen species levels and decreased the mitochondrial membrane
potential in a time-dependent manner as well as activated the
PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy process in CAL 27 cells.
Conclusion: Based on our findings, ZnO NPs may possess potential anticancer
activity toward tongue cancer cells.
Keywords: zinc oxide nanoparticles, mitophagy, tongue cancer; anticancer
therapy