9 5 9 0 3
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

蛋白-2 通过 PI3K/Akt/mTOR 通路在乳腺癌转移中起重要作用
Authors Xia E, Zhou X, Bhandari A, Zhang X, Wang O
Received 16 January 2018
Accepted for publication 24 April 2018
Published 18 June 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 1575—1583
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S162670
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Luzhe Sun
Introduction: Synaptopodin 2 (SYNPO2) is a functioning protein. It has been detected
in many malignancies. But the relation between SYNPO2 and breast cancer (BC) is
unclear.
Materials and methods: In this study, we explored the expression and
function of SYNPO2 in BC. We found that SYNPO2 gene in
BC was downregulated at the transcriptional level in both validated and TCGA
cohorts.
Results: The results revealed that age, lymph node metastasis,
and clinical stage in the validated cohort were related to the expression of
SYNPO2 negatively. Kaplan–Meier analysis showed that patients with lower SYNPO2
expression had a worse overall survival.
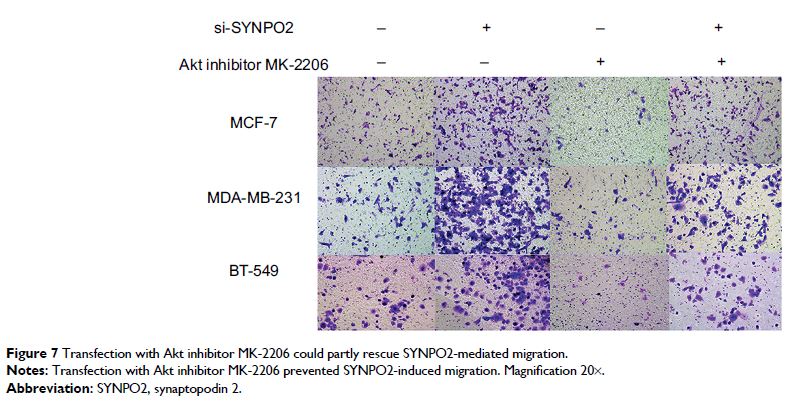
Discussion: We found that migration and invasion were
promoted after knocking down SYNPO2 in MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, BT-549, and
MDA-MB-468. Meanwhile, knockdown of SYNPO2 could enhance PI3K/AKT/mTOR
signaling pathway, which may induce migration and invasion. Our findings reveal
that SYNPO2 was associated with BC.
Keywords: breast cancer,
SYNPO2, metastasis, PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway