108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

INHBA 上调与食管鳞状细胞癌患者预后不良的关联
Authors Lyu S, Jiang C, Xu R, Huang Y, Yan S
Received 18 December 2017
Accepted for publication 10 April 2018
Published 18 June 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 1585—1596
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S160186
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leylah Drusbosky
Purpose: INHBA, which encodes a member
of the TGF-beta superfamily of proteins, has been identified to play a critical
role in different types of cancer. However, its clinical significance in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) has never been reported.
Patients and methods: In this study, we collected 239 ESCC paraffin-embedded
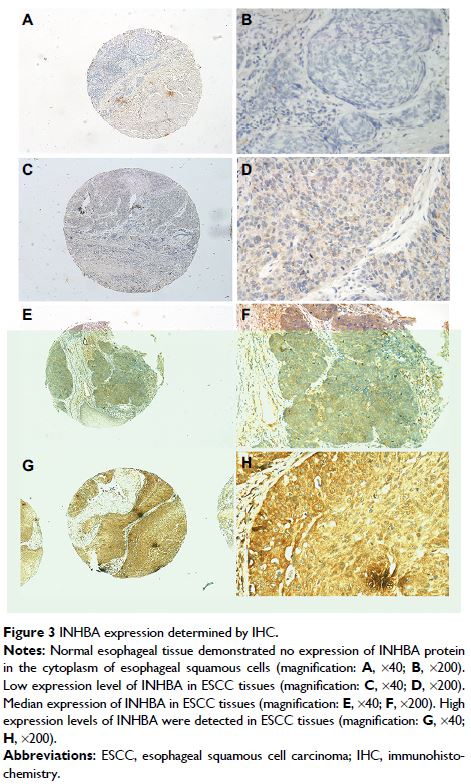
specimens and measured the expression of INHBA with immunohistochemistry (IHC).
The clinical and prognostic significance of INHBA expression was statistically
analyzed. What is more, we conducted a meta-analysis to study the prognostic
value of INHBA expression in multiple types of solid tumors.
Results: The results showed that INHBA expression was observed
predominantly in the cytoplasm of cells in the ESCC specimens. INHBA expression
was closely correlated with N categories (P =0.026).
Kaplan–Meier analysis showed that ESCC patients in the low INHBA expression subgroup
had significantly better prognosis than those with high INHBA level. Subgroup
analysis revealed that INHBA distinguished the disease-free survival (DFS) and
overall survival (OS) when patients were stratified by TNM stage status and N
status. Multivariate analysis results suggested that INHBA expression was an
independent factor that affected OS (HR =1.679, P =0.022) and DFS (HR =1.715, P =0.017). In the meta-analysis,
six papers with 1321 patients were included and patients with high INHBA level
had worse prognosis than patients with low INHBA level (HR 2.50, 95% CI
1.75–3.57, P <0.0001).
Conclusion: High INHBA level predicts poor prognosis in ESCC and
other solid tumors. More studies are required to elucidate the role of INHBA
and its clinical application in cancer settings.
Keywords: INHBA, ESCC,
meta-analysis, prognosis