108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过大黄酸加载的聚乙二醇 - 聚己内酯- 共聚乙烯亚胺纳米粒子进行肾靶向药物递送,用于糖尿病肾病治疗
Authors Chen DF, Han SP, Zhu YQ, Hu F, Wei YH, Wang GW
Received 24 February 2018
Accepted for publication 21 April 2018
Published 19 June 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 3507—3527
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S166445
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Eytan Klausner
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lijie Zhang
Introduction: Diabetic
nephropathy (DN) is the primary root of morbidity and mortality in diabetic
patients. Unfortunately, currently, no effective therapeutic strategies are
available to ameliorate and reverse the progression of DN. Rhein (RH) is an
anthraquinone derivative extracted from herbal medicines with various
pharmacological effects on DN. However, its clinical administration is limited
by its poor solubility, low bioavailability, reduced distribution into the
kidney and adverse effects.
Methods and
results: To improve the delivery of RH into
kidney and the therapeutic effect on DN, we synthesized and utilized
polyethyleneglycol-co -polycaprolactone-co -polyethylenimine triblock
amphiphilic polymers to prepare RH-loaded polyethyleneglycol-co -polycaprolactone-co -polyethylenimine nanoparticles
(PPP-RH-NPs). PPP-RH-NP size was optimized to 75 ± 25 nm for
kidney-targeted drug delivery; the positive zeta potential allowed an effective
cellular uptake and the polyethylenimine amine groups facilitate the endosomal
escape quickly. The distribution and pharmacodynamics of PPP-RH-NPs were
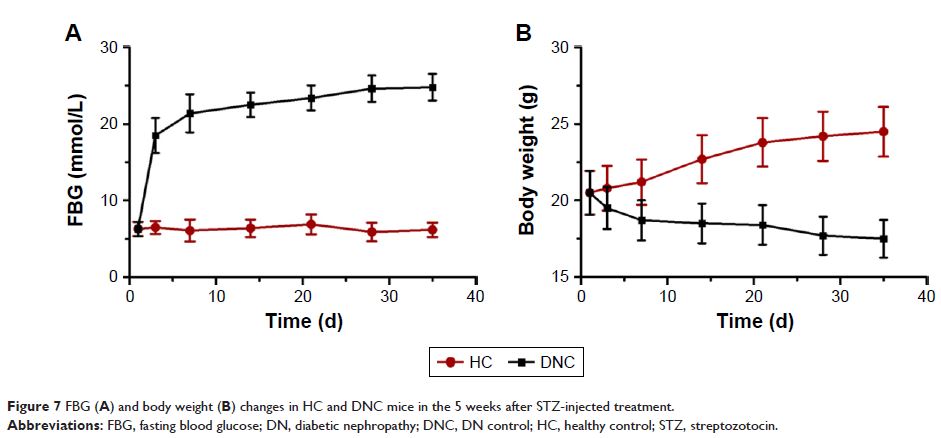
studied in a streptozocin-induced DN model, which explicitly demonstrated
kidney-targeted distribution and improved the therapeutic effects of RH on DN
by ameliorating several pathological indicators.
Conclusion: Therefore, this study not only stimulates further clinical
research on RH but also, more importantly, proposes a promising DN therapy
consisting of an effective kidney-targeted drug delivery.
Keywords: rhein, diabetic nephropathy, polyethyleneglycol-co -polycaprolactone-co -polyethylenimine, nanoparticles, in vitro/vivo
evaluation, targeting drug delivery