108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

STAT3 通过新的 miR-572-MOAP-1 途径诱导结肠直肠癌进展
Authors Wang N, He X, Zhou R, Jia G, Qiao Q
Received 3 December 2017
Accepted for publication 20 April 2018
Published 15 June 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 3475—3484
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S158764
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Purpose: Colorectal
carcinoma (CRC) is among the most common causes of death. Recent studies have
shown that both STAT3 and miR-572 contribute to CRC progression. STAT3 plays an
important role in miRNA expression. Moreover, MOAP-1, which is a pro-apoptotic
protein that induces cell death or apoptosis, has a direct correlation with
miRNA. Therefore, the current study is designed to explore whether miR-572 and
STAT3 are involved in a common pathway and the role of MOAP-1 in this process.
Patients and
methods: The expressions of STAT3, miR-572,
and MOAP-1 in human CRC tissues and multiple cell lines were estimated by
qRT-PCR or Western blot. MTT, transwell migration, and invasion assays were
used to assess cell growth, migration, and invasion, respectively.
Dual-luciferase reporter assay was applied to examine the association between
miR-572 and MOAP-1.
Results: Elevated STAT3 levels were accompanied by increased miR-572 and
decreased MOAP-1 levels in primary CRC specimens and cell lines. STAT3 promoted
CRC cell growth, migration, and invasion via the upregulated expression of
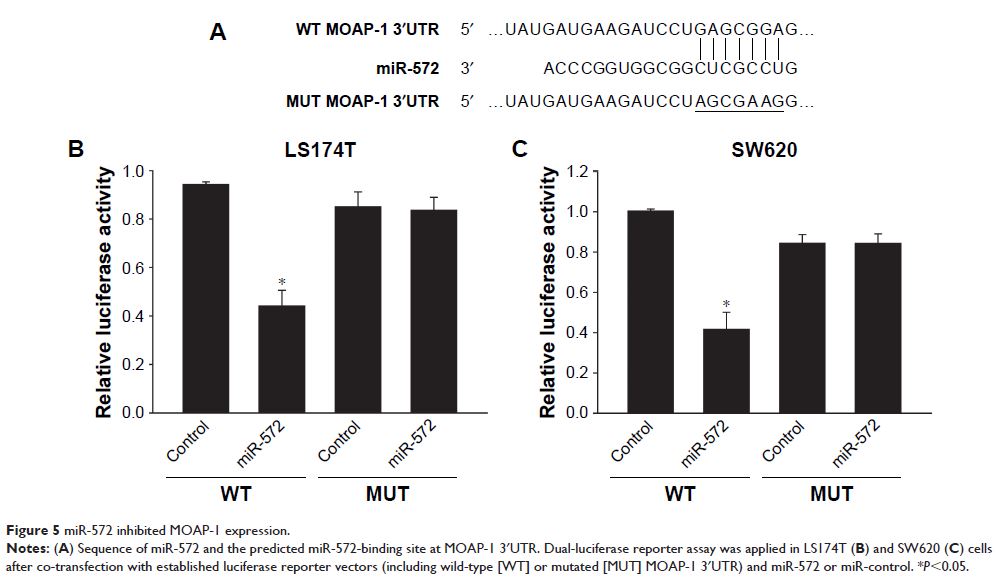
miR-572. Subsequently, miR-572 inhibited MOAP-1 protein expression through an
interaction with its 3'UTR.
Conclusion: Our study proposes a novel STAT3-miR-572-MOAP-1 pathway involved
in the process of CRC progression, which might be a potential target for the
development of new preventive and therapeutic approaches against human
colorectal cancer.
Keywords: colorectal neoplasm, STAT3, MOAP-1, miR-572, tumor progression