108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MALAT1 沉默可通过上调 miR-1 和下调 KRAS 来抑制前列腺癌的进展
Authors Chang J, Xu W, Du X, Hou J
Received 30 January 2018
Accepted for publication 19 April 2018
Published 15 June 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 3461—3473
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S164131
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Narasimha Reddy Parine
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tohru Yamada
Background: Prostate cancer (PC) is the second leading cause of cancer-related
deaths among men. Long noncoding RNA metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma
transcript 1 (MALAT1 ) performed as an oncogene
in multiple cancers including PC. However, the molecular mechanisms of MALAT1
implicated in PC progression have not been thoroughly elaborated.
Materials and
methods: Reverse transcription-quantitative
polymerase chain reaction assay was used to detect the expressions of MALAT1
and microRNA-1 (miR-1). Protein levels of cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase,
cleaved caspase-3, BAX, bcl-2, and KRAS were determined using a western blot
assay. Cell proliferation was assessed by colony formation and MTS assays. Cell
migration capacity was examined by transwell migration assay (Corning
Incorporated, Corning, NY, USA). Apoptosis rate was measured by flow cytometry
via double staining of annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide. Luciferase and RNA
immunoprecipitation assays were employed to explore the relationship among
miR-1, MALAT1, and KRAS.
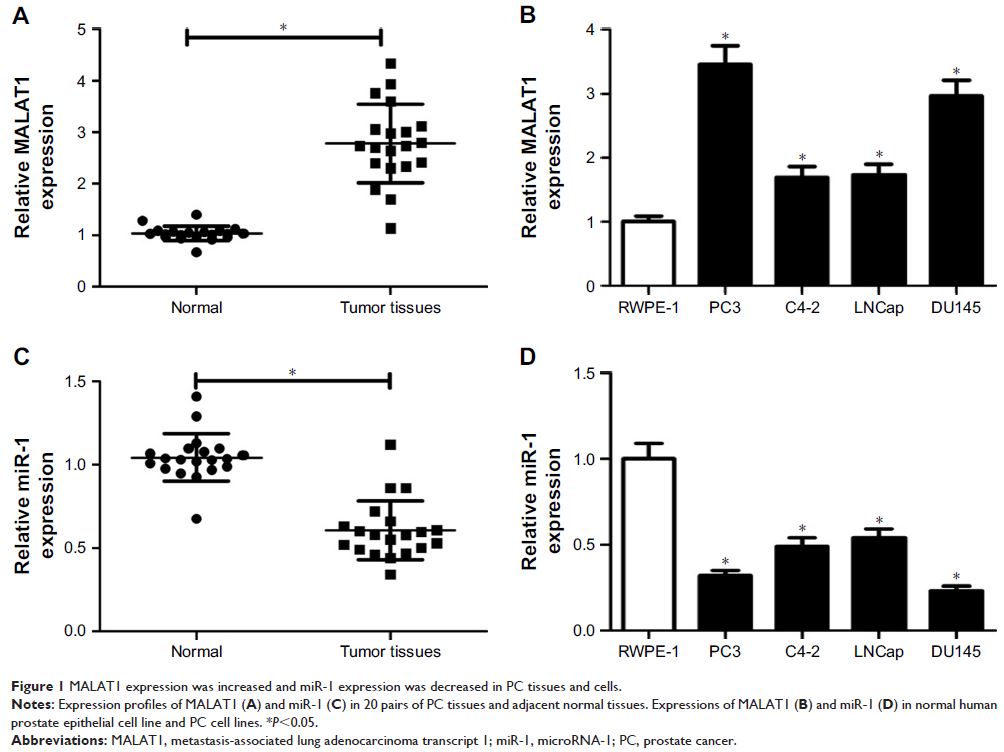
Results: MALAT1 expression was upregulated and miR-1 expression was
downregulated in PC tissues and cell lines. MALAT1 knockdown inhibited cell
proliferation and migration, and promoted cell apoptosis in androgen
receptor-negative DU145 and PC3 cells. Molecular mechanism explorations
disclosed that MALAT1 acted as a molecular sponge of miR-1 in DU145 cells.
Moreover, miR-1 downregulation partly abrogated MALAT1 silencing-mediated
anti-proliferative, antimigratory, and proapoptotic effects in DU145 and PC3
cells. Further investigation revealed that KRAS was a target of miR-1 in DU145
cells. MALAT1 acted as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-1, resulting in the
increase of KRAS expression in DU145 and PC3 cells. Furthermore, miR-1
overexpression hampered proliferation and migration and promoted apoptosis in
DU145 and PC3 cells, while these effects were markedly weakened following KRAS
upregulation.
Conclusion: MALAT1 knockdown inhibited proliferation and migration and
facilitated apoptosis by upregulating miR-1 and downregulating KRAS in androgen
receptor-negative PCa cells, providing a new insight into the molecular basis
of MALAT1 and a potential biomarker or therapeutic target for suppressing
castration-resistant PC.
Keywords: prostate cancer, MALAT1, microRNA-1, KRAS