108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

序贯营养支持对早期重型颅脑损伤患者营养状况及调节性 T 淋巴细胞表达的影响
Authors Jia K, Tong X, Liang F
Received 23 August 2017
Accepted for publication 18 April 2018
Published 14 June 2018 Volume 2018:14 Pages 1561—1567
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S149802
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Prof. Dr. Roumen Kirov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Wai Kwong Tang
Objective: To
investigate the effects of sequential nutritional support on nutritional status
and immune regulation in patients with early severe traumatic brain injury
(STBI).
Patients and
methods: A total of 62 patients diagnosed
with STBI enrolled from Chaoyang Hospital (Beijing, China) from February 2015
to October 2016 were divided into two groups. The observational group (n=34)
was given sequential nutritional support and the control group (n=28) was given
the standard formula of whole protein enteral preparations. The energy supply
for the two groups was 30 kcal/kg/d and protein 1.6 g/kg/d, respectively. The
albumin (ALB), total protein (TP), high-sensitivity C-reactive protein
(Hs-CRP), neuron-specific enolase (NSE), Glasgow Coma Score (GCS), and regulatory
T cells before and after nutritional treatment were measured in both groups.
Results: At the 14th day, the levels of ALB (41.7±4.2 g/L) and TP (70.6±4.9
g/L) were significantly higher than those in the control group (33.5±2.3 g/L
and 62.3±3.9 g/L) (P <0.05). The
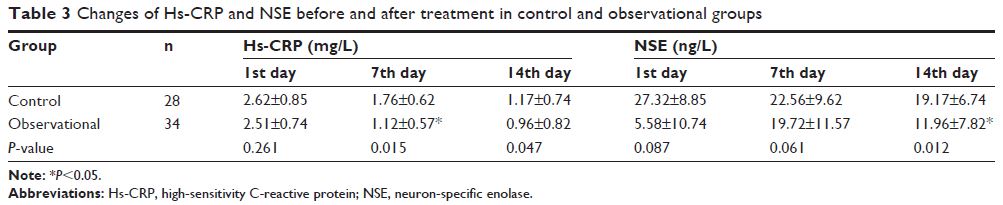
levels of Hs-CRP and NSE were significantly lower in the observational group
(0.96±0.82 mg/L and 11.96±7.82 ng/L) than in the control group (1.17±0.74 mg/L
and 19.17±6.74 ng/L) (P <0.05). The GCS
score in the observational group (11.5±2.9) was significantly higher than that
in the control group (8.1±1.7) (P <0.05). The
percentage of Tregs in the peripheral CD4+ lymphocytes was significantly lower in the observational group
than in the control group (P <0.05).
Conclusion: The effect of sequential nutritional support is better than
conventional nutritional support in patients with STBI. The findings call for
early identification of malnutrition and individual nutritional support.
Keywords: severe traumatic brain injury, enteral nutrition, sequential
nutrition, regulatory T lymphocytes