108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

作为胰腺癌的诊断和预后标志物的双微小 RNA 标记
Authors Yu Y, Feng X, Cang S
Received 2 December 2017
Accepted for publication 17 March 2018
Published 13 June 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 1507—1515
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S158712
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Background and
aim: Some
cancer-specific miRNAs are dysregulated in pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PAAD) and
involved in cell autophagy, differentiation, proliferation, migration,
invasion, and malignant transformation. The aim of our study was to determine a
panel of new diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for PAAD.
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive analysis of global
miRNA-expression profiles and corresponding prognosis information of 168 PAAD
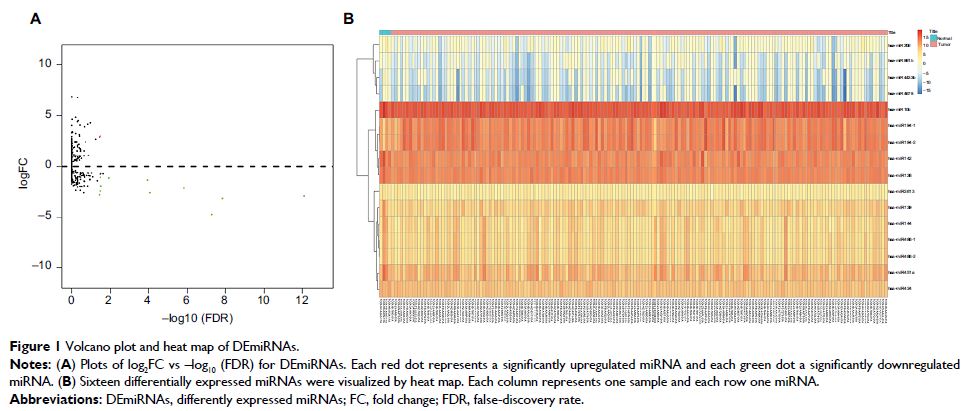
patients from the Cancer Genome Atlas data set. A total of 16 differentially
expressed miRNAs were identified as aberrantly expressed in PAAD, and six of
these were evaluated for use as diagnostic markers for PAAD. Next, we confirmed
a two-miRNA signature significantly associated with PAAD patient diagnosis and
outcome prediction.
Results: The panel of two miRNAs showed outstanding
diagnostic performance, with sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 87.5%.
Finally, we divided the PAAD patients into high-risk and low-risk groups based
on the expression profile of the two miRNAs. Kaplan–Meier analysis demonstrated
that patients in the high-risk group had significantly worse prognosis than patients
in the low-risk group. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis
showed that the two-miRNA signature was an independent prognostic factor for
the overall survival of PAAD patients.
Conclusion: Taken together, the two-miRNA signature may serve
as an accurate and sensitive biomarker for diagnosis and PAAD-outcome
prediction, facilitating the diagnosis and potentially improving treatment
outcome of PAAD.
Keywords: pancreatic
adenocarcinoma, microRNA signature, TCGA, prognosis, diagnosis