108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对作为黑素瘤肿瘤发生标志物的 CD24 的识别
Authors Tang MR, Guo JY, Wang D, Xu N
Received 14 November 2017
Accepted for publication 9 April 2018
Published 12 June 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 3401—3406
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S157043
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
Objective: Cutaneous melanoma (CM)
is a common skin cancer. Surgery is still the primary treatment for CM, as melanoma
is resistant to chemotherapy. In the recent years, it has been found that
cancer stem-like cells (CSCs) are responsible for this drug resistance. CD24 is
a widely used marker to isolate CSCs. In this study, we aimed to analyze the
properties of CD24+ and CD24−subpopulation of melanoma cells.
Materials and methods: We isolated CD24+ cells CSCs
using magnetic-activated cell sorting system. We extracted total RNA and
carried out reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis. We
counted the cell colonies using soft agar assay and assessed the cell invasion
using cell migration assay. We implanted CD24+ or CD24− cells into the flank of non-obese diabetic
severe combined immunodeficiency mice, and measured the tumor volumes every 5
days until the end of the experiment. We carried out immunohistochemical
analysis to study the tissue sections.
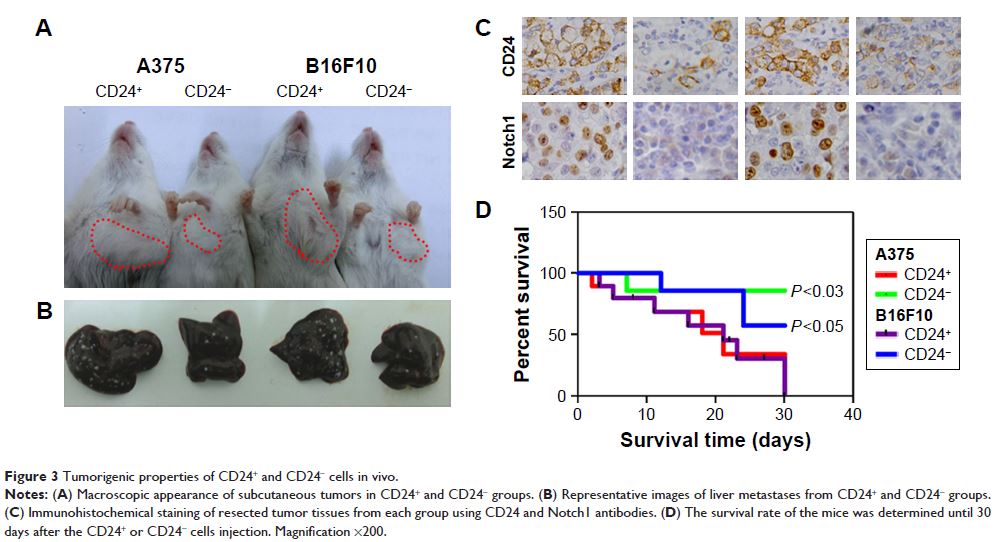
Results: We demonstrated that the CD24+ subpopulation has self-renewal properties in
vitro and in vivo by using soft agar assay and xenograft tumor model. Furthermore,
we confirmed that CD24 expression is accompanied by activation of Notch1
signaling pathway.
Conclusion: This study provides new knowledge on the role of
CD24 in the tumorigenic ability of melanoma.
Keywords: melanoma, CD24,
apoptosis, migration, therapy