108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

聚乙烯亚胺修饰的氢氧化铝纳米粒子增强了树突状细胞的抗原运输和交叉呈递
Authors Dong H, Wen ZF, Chen L, Zhou N, Liu H, Dong S, Hu HM, Mou YB
Received 30 January 2018
Accepted for publication 9 April 2018
Published 7 June 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 3353—3365
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S164097
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Farooq Shiekh
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: The aim of this study was to explore the feasibility of delivering
tumor antigens and enhancing the antigen cross-presentation of dendritic cells
(DCs) by aluminum hydroxide nanoparticle with polyethyleneimine (PEI)
modification (LV@HPA/PEI).
Materials and methods: The LV@HPA nanoparticles were modified by PEI
first, then the influence of LV@HPA/PEI on DCs was examined. The distinct
expression of ovalbumin (OVA) protein transported into DCs by LV@HPA/PEI was
observed by flow cytometry and Western blot. The biocompatibility of
LV@HPA/PEI, maturity and antigen cross-presentation of DCs was observed in
vitro. Tumor derived autophagosomes (DRibbles) combined with LV@HPA/PEI were
loaded into DCs, and DC vaccines were used to immunize mice. The percentage of
CD3+CD8+IFN-γ+ T cells in immunized mice was determined by
flow cytometry. Additionally, the functional properties of the
LV@HPA/PEI-DRibble-DCs vaccine were examined in vivo in PancO2 tumor-bearing
mice.
Results: In our study, we described how LV@HPA/PEI can be
a functionalized antigen delivery system with notable antigen transport effect
and negligible cytotoxicity. It was found that LV@HPA/PEI could be easily
internalized into DCs to assist antigen release into the cytoplasm. In
addition, DCs matured gradually after loading with LV@HPA/PEI-OVA, which
increased significantly the cytokine IL-12 secretion and expression of surface
molecules CD80 and CD86. Interestingly, DCs loaded with LV@HPA/PEI-DRibbles could
promote the activation of tumor-specific T cells both in murine and in human T
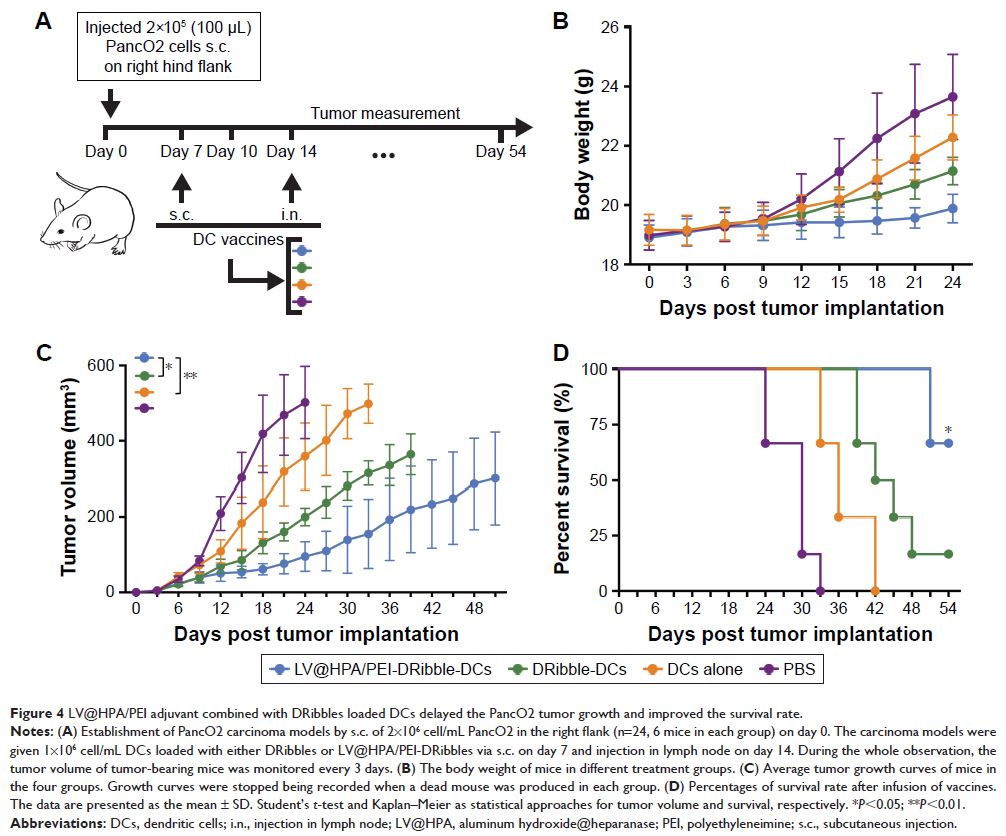
cells. In the following in vivo experiments, the vaccine of
LV@HPA/PEI-DRibble-DCs significantly inhibited tumor growth and improved the
survival rate of the PancO2 tumor-bearing mice.
Conclusion: We established a high-performance anti-tumor vaccine
of DCs loaded with LV@HPA/PEI nanoparticles and tumor-associated antigens in
autophagosomes (DRibbles), which could serve as a therapeutic strategy in
cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: aluminum
hydroxide, antigen delivery, DRibbles, nano-adjuvant, cancer immunotherapy,
autophagosome