108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对 IA 期非小细胞肺癌中楔形切除术与肺段切除术进行比较和综合分析
Authors Xue WF, Duan GC, Zhang XP, Zhang H, Zhao QT, Xin ZF
Received 3 January 2018
Accepted for publication 27 March 2018
Published 7 June 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 3369—3375
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S161367
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Background: Although limited resection was once considered the surgical
treatment for patients with Phase IA non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), there
has been an ongoing controversial surgical indication for wedge resection and
segmentectomy in recent years. The objective of this study was to compare
overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) of segmentectomy and
wedge resection for early stage NSCLC, using a meta-analysis.
Methods: Systematic research was conducted using four online databases to
search for studies published before 2017. The DFS and OS for early stage NSCLC
after segmentectomy and wedge resection were compared. The studies were
selected according to rigorous predefined inclusion criteria, and meta-analyzed
using the log (hazard ratio; ln[HR]) and its standard error (SE) calculations.
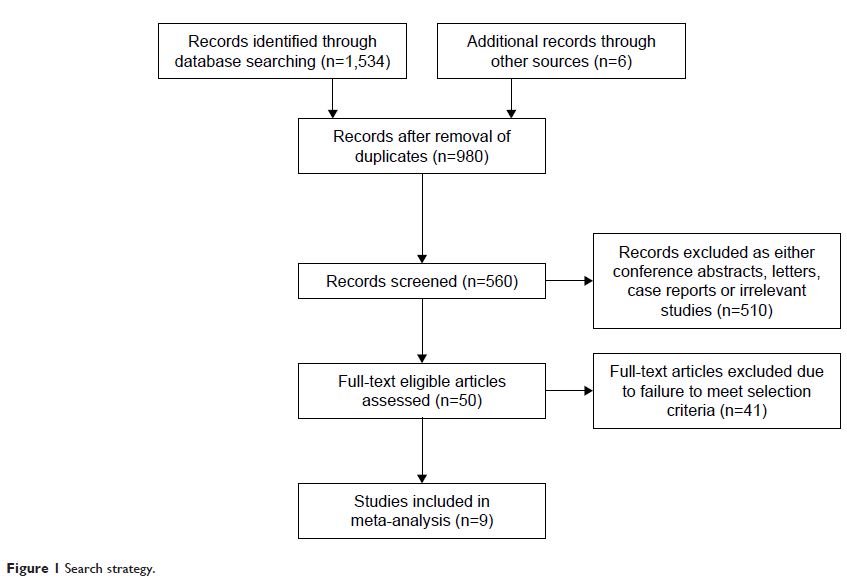
Results: Included in this meta-analysis were nine studies, published from
2006 to 2017, with a total of 7,272 patients. Survival outcome of segmentectomy
was comparable to wedge resections for stage IA lung cancer because of OS
(similar hazard ratio [HR]: 0.93, 95% confidence interval [CI]:
0.83–1.05, P =0.26) and DFS (similar HR: 0.81,
95% CI: 0.60–1.09, P =0.17).
Nevertheless, for stage IA NSCLC with tumor size ≤2 cm, segmentectomy was
superior to wedge resection (combined HR: 0.82, 95% CI: 0.70–0.97, P =0.02). However, there were no
significant differences in OS rates, 1.07 (95% CI: 0.78–1.46, P =0.68), between
segmentectomy and wedge resection for IA NSCLC with a tumor size of ≤1 cm.
Conclusion: This study concluded that segmentectomy could achieve better OS
than wedge resection for stage IA NSCLC with a tumor size of ≤2 cm.
However, surgeons could conduct segmentectomy and wedge resection for NSCLC
≤1 cm according to patient profile and the location of tumor. These
results should be confirmed by further randomized clinical trials.
Keywords: segmentectomy, wedge resection, IA NSCLC, meta-analysis