108899
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

以 ECG 定位的 PICC 尖端位置验证在心房颤动患者中应用的安全性和准确性
Authors Gao Y, Liu Y, Zhang H, Fang F, Song L
Received 8 November 2017
Accepted for publication 17 April 2018
Published 6 June 2018 Volume 2018:14 Pages 1075—1081
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S156468
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Hoa Le
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
Background: Tip position verification of peripherally inserted central
catheters (PICCs) is essential to the use of the catheter. Postprocedural chest
X-ray as the “gold standard” practice for PICC tip confirmation can lead to a
significant delay for patient IV therapy, cost more, and lead to radiation
exposure for both patients and staffs. Intracavitary electrocardiogram
(IC-ECG)-guided PICC placement which provides real-time tip confirmation during
the insertion procedure has been widely used. However, safety and accuracy of
ECG for abnormal surface ECG patients, such as patients with atrial fibrillation
(AF), have not been reported.
Objective: To determine the safety and accuracy of IC-ECG technique for PICC
tip position verification among the patients with AF.
Patients and
methods: A prospective cohort study was
conducted in a teaching and tertiary referral hospital with more than 3,600
beds in Qingdao, People’s Republic of China. Adult patients with diagnosis of
AF who need a PICC for infusion from June 2015 to May 2017 were enrolled in the
study. For every included patient with AF, ECG was used to detect the PICC tip
position during catheterization and X-ray was done to confirm the tip position
as the “gold standard” after PICC insertion. The effectiveness and accuracy of
ECG-guided catheter tip positioning and chest X-ray confirmation were compared.
Results: Totally, 118 AF patients with 118 PICCs were enrolled (58 male and 60
female, age range 50–89 years old). There was no catheterization-related
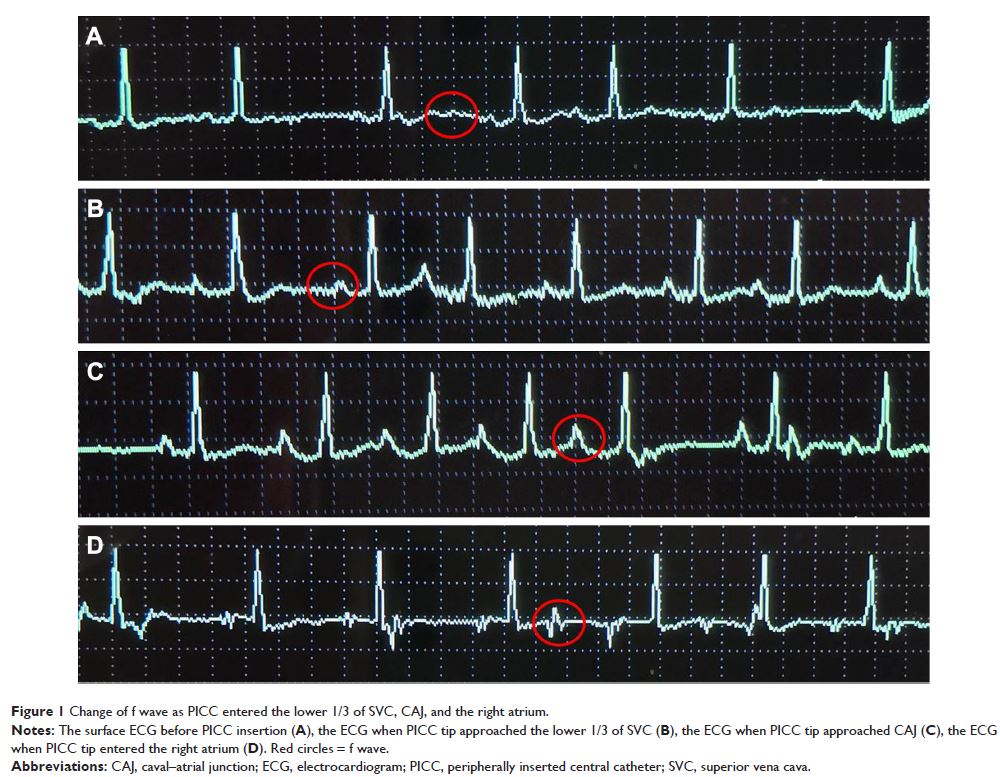
complication. When the catheter entered the lower 1/3 of superior vena cava,
the amplitude of f wave reached the maximum. There was no statistical
difference between X-ray PICC tip position verification and IC-ECG PICC tip
position verification among patients with AF (χ 2=1.31, P =0.232). Utilizing
the cutoff point of f wave change ≥0.5 cm, a sensitivity of 0.94, a specificity
of 0.71, a positive predictive value of 0.98, and a negative predictive value
of 0.42 were observed. The area under the receiver operating characteristic
curve was 0.909 (95% CI: 0.810–1.000).
Conclusion: The ECG-guided technique represents a safe and accurate technique to
verify the position of PICC tip in patients with AF and could potentially
remove the requirement for postprocedural chest X-ray among the patients with
AF.
Keywords: peripherally inserted central catheter, PICC, tip position,
electrocardiograph, ECG, patients with atrial fibrillation