108899
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA 00152(LINC00152)的敲除可抑制人视网膜母细胞瘤的进展
Authors Li S, Wen D, Che S, Cui Z, Sun Y, Ren H, Hao J
Received 20 December 2017
Accepted for publication 12 March 2018
Published 6 June 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 3215—3223
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S160428
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Background: A growing body of
evidence supports the involvement of long noncoding RNA 00152 (LINC00152) in
the progression and metastasis of multiple cancers. However, the exact roles of
LINC00152 in the progression of human retinoblastoma (RB) remain unknown. We
explored the expression and biological function of human RB.
Materials and methods: The expression level of LINC00152 in RB tissues and
cells was analyzed using quantitative real-time PCR. The function of LINC00152
was determined using a series of in vitro assays. In vivo, a nude mouse model
was established to analyze the function of LINC00152. Gene and protein
expressions were detected using quantitative real-time PCR and Western blot
assays, respectively.
Results: The expression of LINC00152 mRNA was upregulated
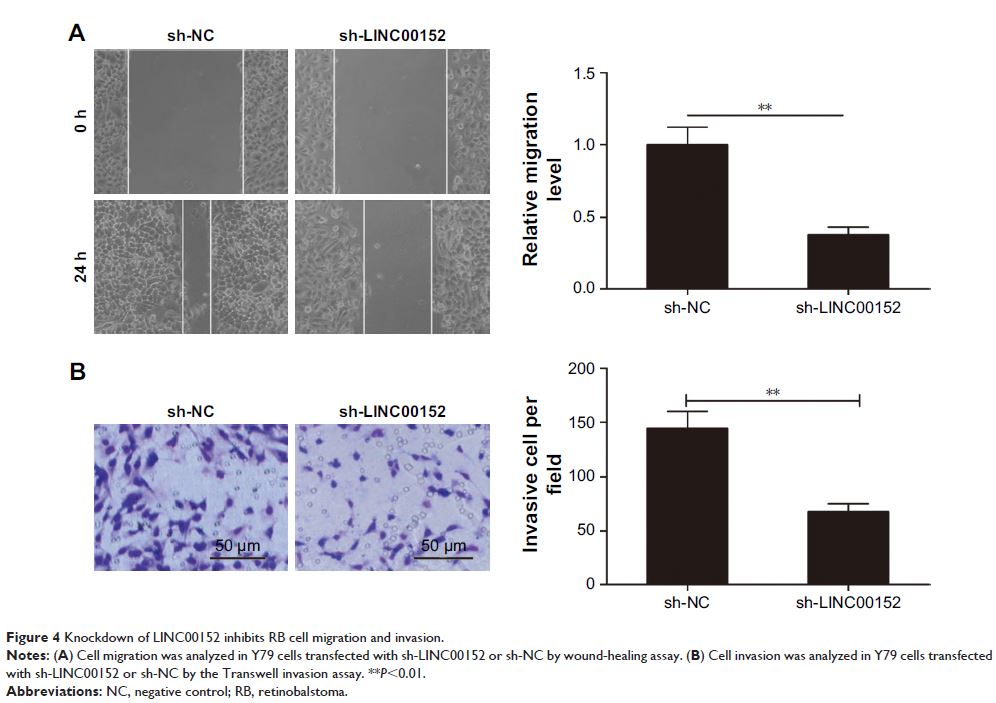
in RB tissues and cell lines. Knockdown of LINC00152 significantly inhibited
cell proliferation, colony formation, migration, and invasion and promoted cell
apoptosis and caspase-3 and caspase-8 activities in vitro, as well as
suppressing tumorigenesis in vivo. We identified several genes related to
proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion including Ki-67, Bcl-2, and MMP-9 that
were transcriptionally inactivated by LINC00152.
Conclusion: Taken together, these data implicate LINC00152
as a therapeutic target in RB.
Keywords: retinoblastoma,
LINC00152, proliferation, invasion