108899
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

应用定量蛋白质组学确定 PGAM1 作为推测的胰腺导管腺癌转移治疗靶标
Authors Liu X, Weng Y, Liu P, Sui Z, Zhou L, Huang Y, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Tan X
Received 13 January 2018
Accepted for publication 26 March 2018
Published 6 June 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 3345—3357
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S162470
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Background: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is an aggressive
gastrointestinal cancer characterized by an extremely low survival rate because
of early metastasis. Identifying satisfactory therapeutic targets associated
with metastasis is crucial to improve the treatment effect of PDAC.
Materials and methods: In this research, we used stable isotope
labeling by amino acids in cell culture, 1-dodecyl-3-methylimidazolium
chloride-assisted sample preparation method preparing protein sample and
nano-reversed-phase liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry
analysis to perform the comparative proteomics of two homologous hamster
pancreatic cancer cell lines that are different in metastatic ability: PC-1.0
(highly metastatic) and PC-1 (weakly metastatic). Verifications are through
immunohistochemistry on clinical human PDAC pathologic tissues as well as by
Western blot of human pancreatic cancer cell lines. siRNA silencing methods
were used to study the effect of molecules on invasion and metastasis of
pancreatic cancer cell lines.
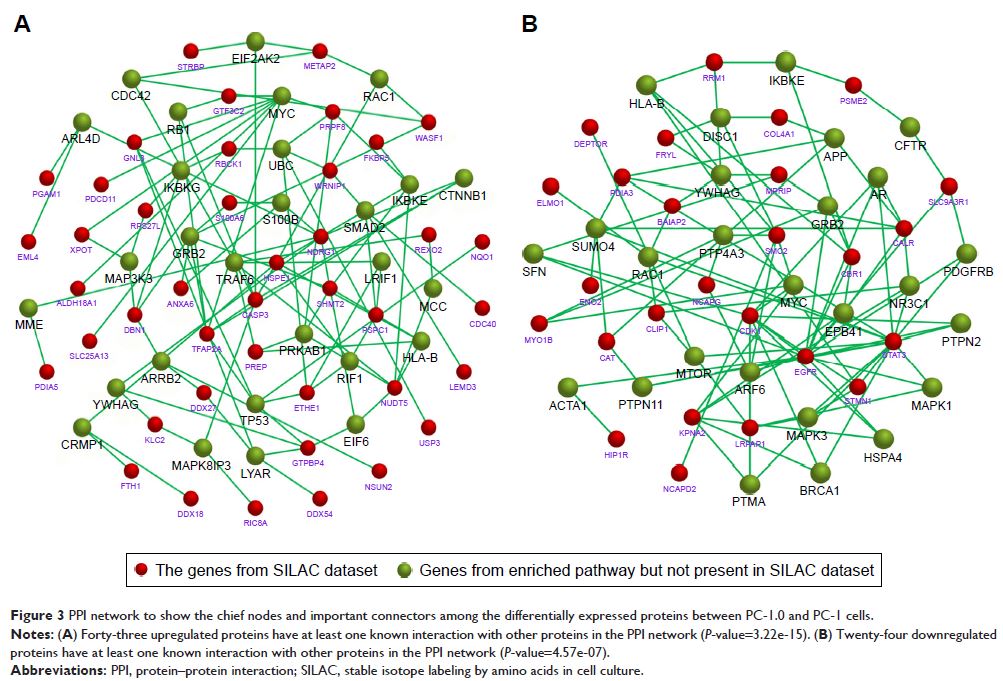
Results: Bioinformatic analysis indicated that a total of
141 differentially expressed proteins (82 upregulated and 59 downregulated in
PC-1.0 cells) were identified showing obviously differential expression
(>1.5-fold change). These differentially expressed proteins were involved in
a number of different biologic functions, metabolic pathways, and
pathophysiologic processes. Phosphoglycerate mutase 1 (PGAM1) and HSPE1 are the
top two upregulated proteins, and PDIA3 and CALR are the top two downregulated
proteins in PC-1.0 cells compared to PC-1 cells. PGAM1 and HSPE1 showed higher
expressions in PDAC tissue with clinical metastasis and highly metastatic
pancreatic cancer cell lines PC-1.0 and Aspc-1. PDIA3 and CALR showed higher
expressions in weakly metastatic pancreatic cancer cell lines PC-1 and Capan-2.
The Western blot results were consistent with the MS quantification data.
Silencing PGAM1 was found to decrease the migration and invasion of pancreatic
cancer cell lines with statistical significance, especially in highly
metastatic PC-1.0 and Aspc-1 cell lines.
Conclusion: These data indicated that PGAM1 may be a
potential therapeutic target for PDAC metastasis.
Keywords: SILAC, PDAC,
metastasis, PGAM1