108899
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

由 siRNA 干扰导致的 AQP-5 基因沉默对乳腺癌细胞化疗敏感性的影响
Authors Li X, Pei B, Wang H, Tang C, Zhu W, Jin F
Received 19 December 2017
Accepted for publication 5 March 2018
Published 6 June 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 3359—3368
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S160313
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Objectives: Based on the
functionality of AQP-5 characterized in various physiological processes, our
study aimed to investigate the effect of AQP-5 silencing by siRNA interference
on chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells.
Materials and methods: The expression levels of AQP-5 mRNA in different
experimental groups were measured by reverse transcription PCR. The
chemosensitivity of the cells to adriamycin (ADR) was detected by a CCK-8 kit.
Cell invasion, migration, and apoptosis were assessed. Western blot was used to
detect the expression levels of AQP-5, drug resistance-related protein, and
apoptosis-related protein.
Results: The expression level of AQP-5 in MCF-7/ADR cells
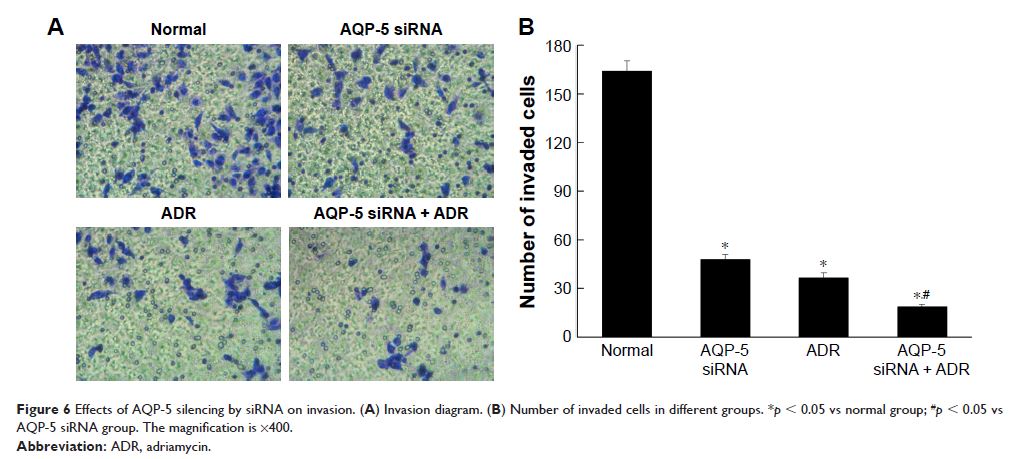
was significantly reduced by AQP-5 siRNA transfection. The invasion and
migration were significantly reduced in MCF-7/ADR after AQP-5 siRNA
interference. AQP-5 silencing significantly increased the chemosensitivity of
MCF-7/ADR cells to ADR and activated caspase-dependent apoptosis in MCF-7/ADR
cells. AQP-5 silencing also decreased the expression levels of drug
resistance-related proteins (P-gp and GST-Π).
Conclusion: The inhibition of AQP-5 expression may reverse
the drug resistance and enhance the chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells.
Keywords: aquaporin 5,
breast cancer, ADR, chemosensitivity, apoptosis