108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CLEC3A 的过表达促进乳腺浸润性导管癌的肿瘤进展和不良预后
Authors Ni J, Peng Y, Yang F, Xi X, Huang X, He C
Received 2 January 2018
Accepted for publication 19 March 2018
Published 5 June 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 3303—3312
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S161311
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
Introduction: The aim of this study was to evaluate the expression of C-type
lectin domain family 3 member A (CLEC3A) and its clinical significance in
breast invasive ductal cancer (IDC) as well as its effect on breast cancer (BC)
cell proliferation and metastasis. In this study, the level of CLEC3A
expression in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) datasets was analyzed.
Materials and
methods: Clinical collected samples and BC
cells were measured using quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain
reaction. Its correlations with patients’ clinicopathological characteristics
were analyzed by Pearson’s chi-squared test. Overall survival (OS) analysis was
performed by the Kaplan–Meier method and Cox’s proportional-hazards model. BC
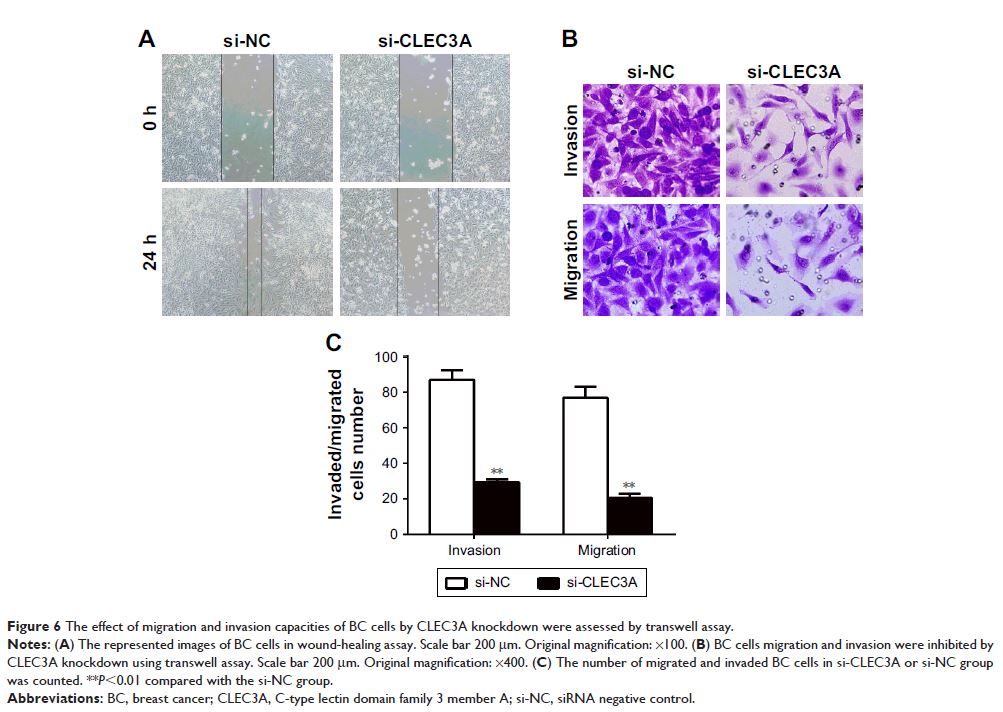
cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by CLEC3A knockdown were assessed
using Cell Counting Kit-8 and colony formation assay, wound healing model and
transwell assay, respectively, in BT474 cell line. Activities of survival
factors and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT)
signaling were measured by testing key molecules using Western blot
assay.
Results: CLEC3A expression was markedly higher in breast IDC tissues than
normal breast tissues or adjacent normal tissue. Patients with high CLEC3A
expression related to higher lymph node and poorer OS of breast IDC. CLEC3A
knockdown by siRNA could inhibit the BC cells BT474 proliferation, migration,
and invasion, together with a decrease in expression of key proteins in
survival factors and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
Conclusion: Elevated CLEC3A expression may correlate with breast IDC
metastatic potential and indicated a poor prognosis in breast IDC. CLEC3A
knockdown inhibited BC cell growth and metastasis might be through suppressing
PI3K/AKT signaling activity. These findings unravel that CLEC3A is a promising
therapeutic target for BC in the future.
Keywords: breast cancer, proliferation, migration, invasion, overall
survival, survival factor, PI3K/AKT