108899
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

针对蜂毒素的一种仿生纳米颗粒类毒素疫苗
Authors Kang T, Li C, Du T, Wu Y, Yang Y, Liu X, Zhang Q, Xu X, Gou M
Received 7 November 2017
Accepted for publication 24 January 2018
Published 1 June 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 3251—3261
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S156346
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
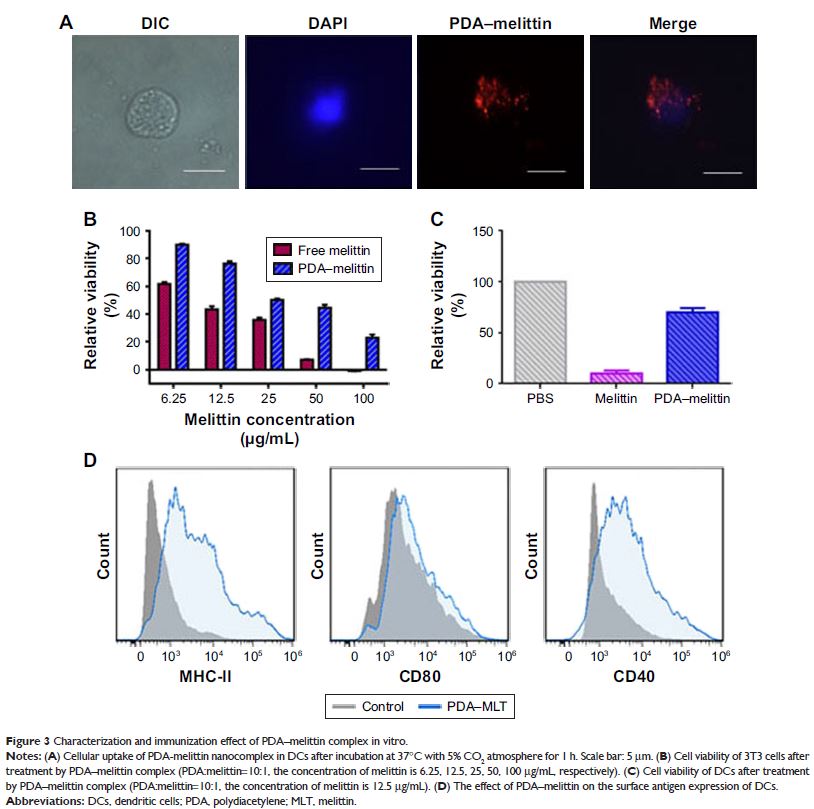
Background: Melittin, the main active peptide ingredient of bee venom, can
cause severe cell membrane lysis due to its robust interaction with negatively
charged phospholipids. So far, no effective anti-melittin vaccine has been
developed to protect people from undesired melittin intoxication.
Methods: Herein, we prepared a polydiacetylene (PDA)
nanoparticle with cell membrane-mimic surface to complex melittin, forming an
anti-melittin vaccine (PDA–melittin).
Results: PDA nanoparticles could effectively combine with
melittin and neutralize its toxicity. PDA–melittin nanocomplex is demonstrated
to enhance melittin uptake by DCs and stimulate strong melittin-specific
immunity. Mice immunized with PDA–melittin nanocomplex showed higher survival
rate after exposion to melittin than untreated mice.
Conclusion: The PDA–melittin nanocomplex can efficiently and
safely generate a specific immunity against melittin to protect body from
melittin intoxication, providing a new method with potential clinical
application for the treatment of melittin intoxication.
Keywords: PDA nanoparticles,
melittin, toxoid vaccine, immunity