108899
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

As2O3 和 AZT 联合应用对 Egr-1 基因沉默后肝癌 HepG2 细胞增殖抑制和凋亡诱导的影响
Authors Zhao C, Wang M, Liu Y, Liang YJ, Han L, Chen C
Received 25 October 2017
Accepted for publication 4 February 2018
Published 1 June 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 3293—3301
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S155169
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Ashok Kumar Pandurangan
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jianmin Xu
Context: Previous
studies have demonstrated that 3´-azido-3´-deoxythymidine (AZT) and arsenic
trioxide (As2O3), traditional chemotherapy agents, can synergically inhibit the growth
of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying
As2O3 and AZT anti-hepatoma activity are unknown.
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the role of early growth response
protein 1 (Egr-1) in the process of As2O3 combined with AZT
inhibiting proliferation and inducing apoptosis of human hepatocellular
carcinoma HepG2 cells, and explore the possible mechanism.
Materials and
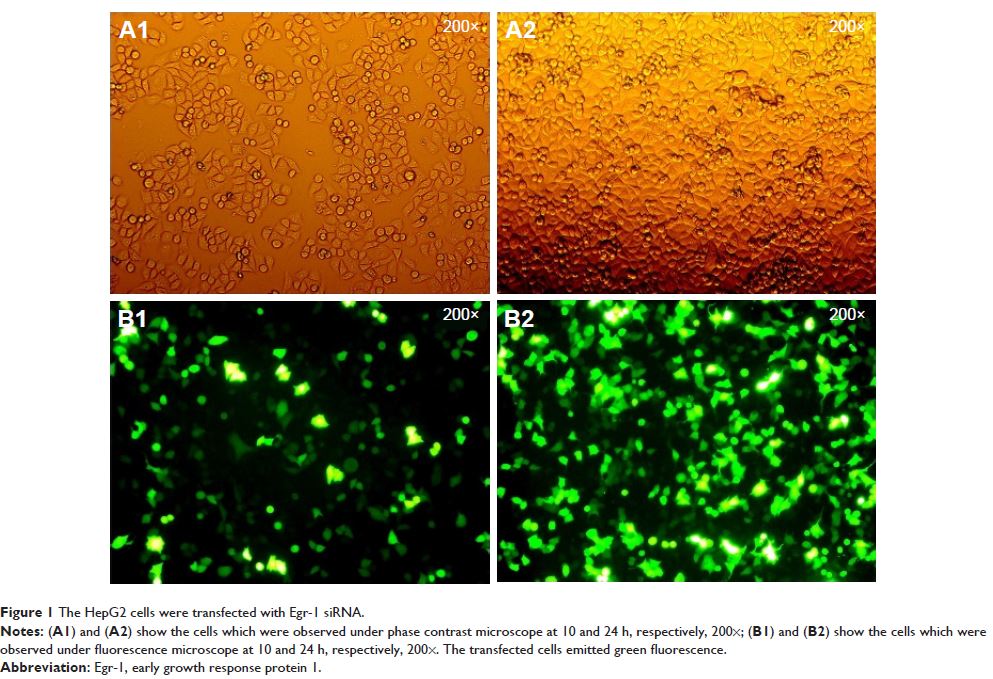
methods: The expression of Egr-1 was silenced
using siRNA, and then HepG2 cells were treated with As2O3 (2 μM) and AZT
(20 μM). The rates of cell inhibition and apoptosis were determined by the
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazoliumbromide (MTT) method and
flow cytometry, respectively. The mRNA and protein expression of p53,
caspase-3, and Egr-1 were detected by real-time quantitative polymerase chain
reaction and Western blotting, respectively.
Results: The inhibitory rate of As2O3 (2 μM)
combined with AZT (20 μM) on proliferation of HepG2 cells was significantly
higher than that of As2O3 alone. The
combination index (CI) values were 0.2
Conclusion: The present results show that AZT
could increase the sensitization of As2O3 for inhibiting
proliferation and promoting apoptosis of HepG2 cells through regulating the
expression of Egr-1, which may control the expression of p53 and caspase-3.
Keywords: HepG2, As2O3, AZT, Egr-1,
proliferation, apoptosis