108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长期非编码 RNA CASC2 在人恶性肿瘤中的预后价值及临床意义:一项综合分析
Authors Cai J, Zuo X, Chen Z, Zhao W, Zhu Y, Zhang Z, Ye X
Received 3 January 2018
Accepted for publication 22 March 2018
Published 31 May 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 1403—1412
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S161373
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Luzhe Sun
Purpose: This meta-analysis
aimed to assess the prognostic value of long noncoding RNA cancer
susceptibility candidate 2 (CASC2) in human tumors.
Materials and methods: We searched the available databases up to
December 2017. Pooled hazard ratios (HRs) and the corresponding 95% confidence
intervals (CIs) were used to examine the prognostic impact of CASC2 on overall
survival (OS) in patients diagnosed with malignancies.
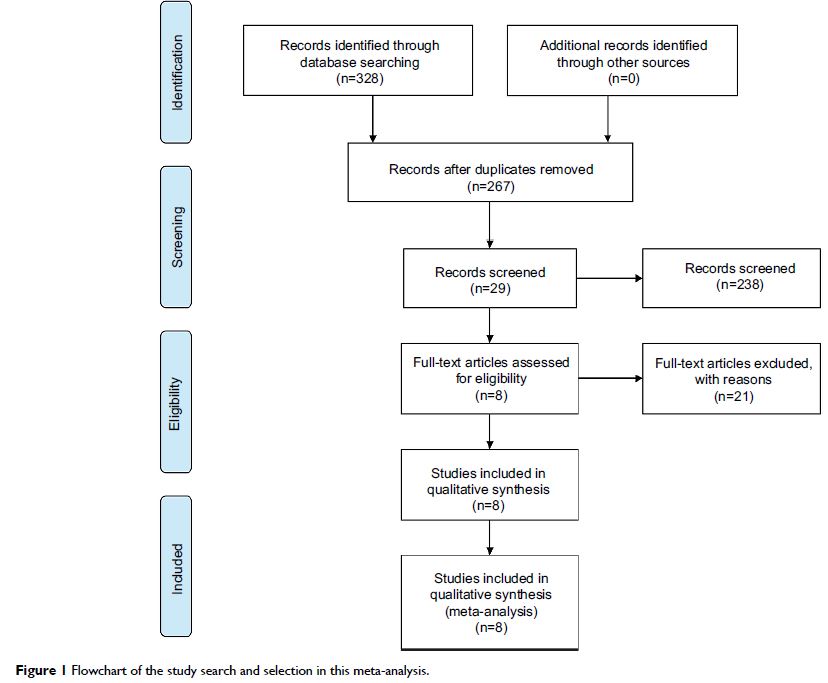
Results: A total of eight studies with 663 cancer
patients were enrolled. Our results showed that high CASC2 expression level was
associated with a favorable OS (HR=0.437, 95% CI: 0.345–0.554). The significant
results were not altered by stratified analysis according to cancer type,
sample size, follow-up months, and HR estimation method. A significant
association of glioma tumor stage with CASC2 expression was detected (III–IV vs
I–II: odds ratio=2.126, 95% CI: 1.032–4.378). CASC2 could be used as an
independent prognostic factor for OS (HR=0.450, 95% CI: 0.336–0.602).
Sensitivity analysis showed that no single study changed the pooled results
significantly. Begg’s funnel plot and Egger’s test showed that no publication
bias was detected.
Conclusion: High
expression level of CASC2 is associated with favorable survival outcome for
cancer patients, and CASC2 could be used as a prognostic predictor for cancers.
Keywords: CASC2, long
noncoding RNA, prognosis, meta-analysis