108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长顺序非编码 RNA 在顺铂耐药中的新兴作用
Authors Hu Y, Zhu QN, Deng JL, Li ZX, Wang G, Zhu YS
Received 25 November 2017
Accepted for publication 3 March 2018
Published 28 May 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 3185—3194
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S158104
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
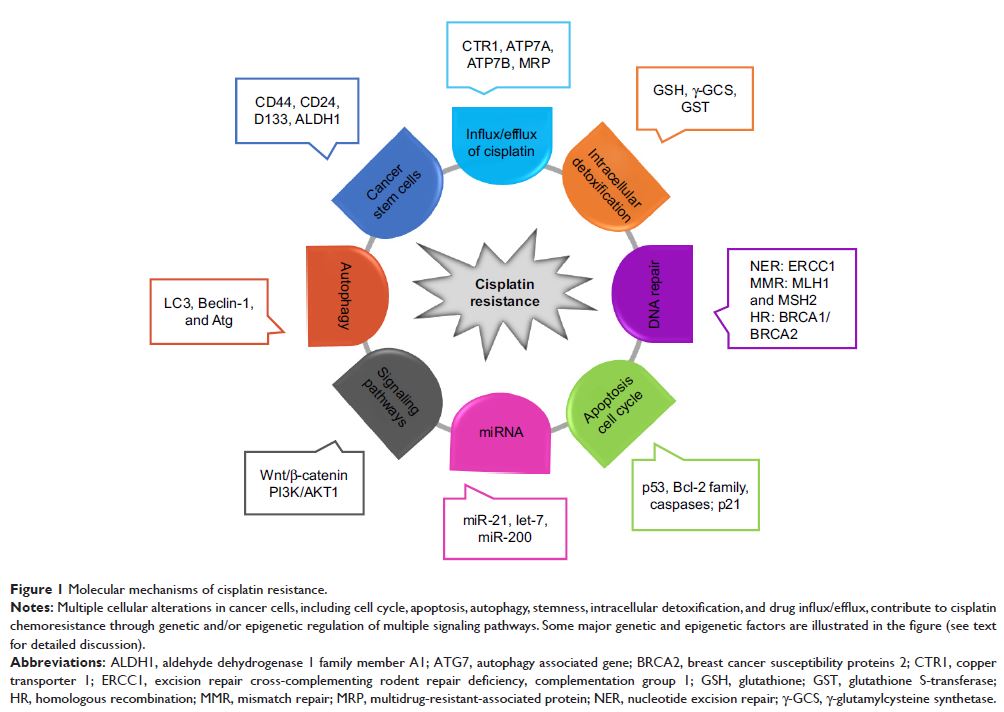
Abstract: Cisplatin (CDDP) is one of the most commonly used chemotherapy
drugs for the treatment of various cancers. Although platinum-based therapies
are highly efficacious against rapidly proliferating malignant tumors, the
development of CDDP resistance results in significant relapse as well as
decreased overall survival rates, which is a significant obstacle in CDDP-based
cancer therapy. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are involved in cancer
development and progression by the regulation of processes related to chromatin
remodeling, transcription, and posttranscriptional processing. Emerging
evidence has recently highlighted the roles of lncRNAs in the development of
CDDP resistance. In this review, we discuss the roles and mechanisms of lncRNAs
in CDDP chemoresistance, including changes in cellular uptake or efflux of a
drug, intracellular detoxification, DNA repair, apoptosis, autophagy, cell
stemness, and the related signaling pathways, aiming to provide potential
lncRNA-targeted strategies for overcoming drug resistance in cancer therapy.
Keywords: cisplatin,
lncRNAs, chemoresistance, cancer