108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-134 通过靶向 Mnks 可提高阿糖胞苷在急性骨髓性白血病细胞中的抗肿瘤作用
Authors Chen K, Chen Y, Chen Z, Shi Y, He Z, Ding B, Wang C, Yu L
Received 7 June 2017
Accepted for publication 6 September 2017
Published 25 May 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 3141—3147
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S143465
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Ru Chen
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Abstract: The relapse and
resistance to cytarabine (Ara-C) therapy is still a dominating obstacle to the
successful clinical treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Recent studies
have shown that dysregulation of miRNAs might modulate the resistance of cancer
cells to anticancer drugs; yet, the mechanism is not fully understood. In this
study, we showed a significant downregulation of miR-134 in human
multidrug-resistant leukemia cells and relapsed/refractory AML patient samples.
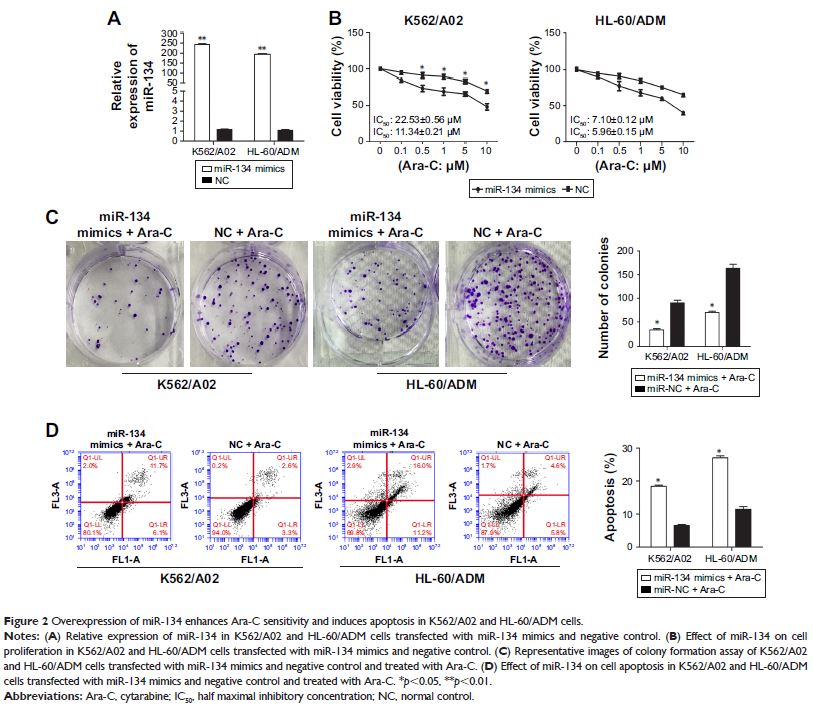
Overexpression of miR-134 sensitized K562/A02 and HL-60/ADM cells to Ara-C,
inhibited cell colony formation, and enhanced the ability of Ara-C to induce
apoptosis. Mechanistic analyses revealed that Mnks was a putative target of
miR-134, which was inversely correlated with miR-134 expression in human multidrug-resistant
leukemia cells and relapsed/refractory AML patient samples. Further
investigation showed that miR-134 increased the antitumor effects of Ara-C
through inhibiting phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E and
downregulating Mcl-1 and bcl2, which was independent of p38 and Erk1/2
activation. Taken together, our results demonstrate that miR-134 plays a
pivotal role in AML Ara-C resistance through increasing cell sensitivity to
Ara-C and promoting apoptosis by targeting Mnks.
Keywords: miR-134, acute
myeloid leukemia, Mnks, eIF4E, apoptosis