108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

白藜芦醇通过抑制 COX-2 的表达来抑制 A549 细胞的增殖
Authors Li X, Li F, Wang FF, Li JF, Lin CZ, Du JX
Received 20 November 2017
Accepted for publication 5 March 2018
Published 22 May 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 2981—2989
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S157613
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Purpose: The aim was to
investigate resveratrol effects on A549 cells proliferation.
Methods: A total of 104 lung adenocarcinoma tissues and
nontumor tissues were collected. BEAS-2B cells were cultured in RPMI 1640
medium (group A). A549 cells were treated with RPMI 1640 medium containing
different resveratrol concentrations. A549 cells were transfected and grouped
as follows: blank group, siRNA-negative control group, siRNA-COX-2 group and
resveratrol + siRNA-COX-2 group. qRT-PCR and Western blot were conducted to
detect COX-2 expression. MTT assay,
soft agar clone assay and flow cytometry were performed to assess proliferation
and cell cycle.
Results: The relative expression of COX-2 mRNA was significantly
increased in lung adenocarcinoma tissues (P <0.01) and it
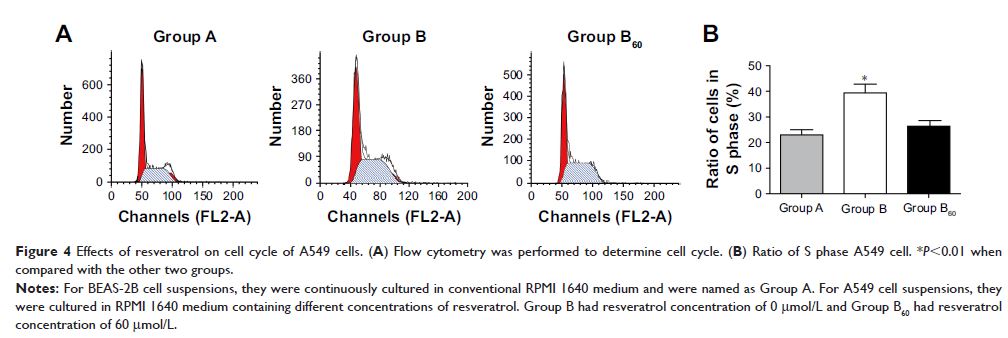
was closely related with clinical stages. Resveratrol at 60 µmol/L
significantly inhibited A549 cells proliferation, S phase cells proportion
and COX-2 expression (P <0.01). COX-2 expression in
siRNA-COX-2 group was significantly lower than that in blank group and
siRNA-negative control group (P <0.01). OD570 values, colony formation rate and S phase cells
proportion of resveratrol + siRNA-COX-2 group were much lower than those of
other groups (P <0.01).
Conclusion: Resveratrol inhibits A549 cells proliferation by
inhibiting COX-2 expression.
Keywords: resveratrol, COX-2 expression, A549 cell,
proliferation