108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

乳铁蛋白和 RGD 共同修饰的替莫唑胺,以及长春新碱 - 共轭纳米结构脂质载体用于脑胶质瘤病联合治疗
Authors Zhang J, Xiao X, Zhu J, Gao Z, Lai X, Zhu X, Mao G
Received 30 December 2017
Accepted for publication 22 March 2018
Published 22 May 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 3039—3051
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S161163
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Mohankandhasamy Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Purpose: Glioblastoma
multiforme (GBM) is the most common malignant brain tumor originating in the
central nervous system in adults. Based on nanotechnology such as liposomes,
polymeric nanoparticles, and lipid nanoparticles, recent research efforts have
been aimed to target drugs to the brain.
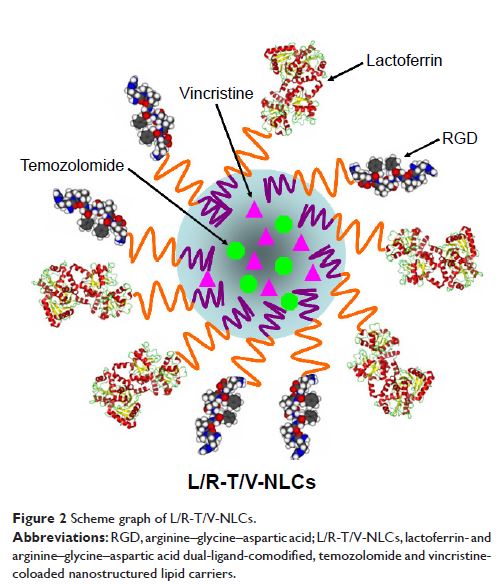
Methods: In this study, lactoferrin- and arginine–glycine–aspartic acid (RGD)
dual-ligand-comodified, temozolomide and vincristine-coloaded nanostructured
lipid carriers (L/R-T/V-NLCs) were introduced for GBM combination therapy. The
physicochemical properties of L/R-T/V-NLCs such as particle size, zeta
potential, and encapsulated efficiency are measured. The drug release profile,
cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, tissue distribution, and antitumor activity of
L/R-T/V-NLCs are further investigated in vitro and in vivo.
Results: L/R-T/V-NLCs were stable with nanosize and high drug encapsulation
efficiency. L/R-T/V-NLCs exhibited sustained-release behavior, high cellular
uptake, high cytotoxicity and synergy effects, increased drug accumulation in
the tumor tissue, and obvious tumor inhibition efficiency with low systemic
toxicity.
Conclusion: L/R-T/V-NLCs could be a promising drug delivery system for glioblastoma
chemotherapy.
Keywords: gliomatosis cerebri, combination therapy, nanostructured lipid
carriers, lactoferrin, arginine–glycine–aspartic acid peptide, vincristine,
temozolomide