108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

治愈性切除术后动脉内化疗改善了 2-3 期胆囊癌的存活率
Authors Chen C, Feng W, Zheng Y, Bao Y, Feng M
Received 22 February 2018
Accepted for publication 12 April 2018
Published 22 May 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 2975—2979
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S166246
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
Objective: To investigate the
impact of postresection intra-arterial chemotherapy (IAC) on prognosis of stage
2–3 gallbladder cancer (GBC) after curative resection.
Methods: Between May 2010 and August 2014, 76 cases of
GBC accepted curative surgery in our center and were pathologically staged as
2–3. After resection, 37 underwent 4 courses of intravenous chemotherapy (IVC)
following 2 courses of IAC (ART group), and 39 received 6 courses of IVC (SYS
group). Both the IAC and IVC regimens consisted of oxaliplatin (85 mg/m2) on day 1 and gemcitabine (800 mg/m2) on day 1 and day 8. Chemotherapy-related
complications, disease-free survival (DFS), overall survival (OS), and hepatic
metastases-free survival (HMFS) were retrospectively analyzed.
Results: Patient characteristics and chemotherapy
complications did not differ between the two groups. There was no significant difference
in 3-year DFS of the two groups (p =0.0822,
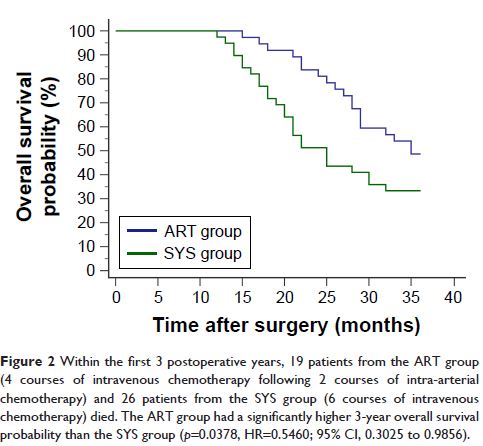
HR=0.6270; 95% CI, 0.3627 to 1.0838). The ART group had significantly higher
3-year OS (p =0.0378, HR=0.5460; 95% CI,
0.3025 to 0.9856) and 3-year HMFS (p =0.0414,
HR=0.5187; 95% CI, 0.2706 to 0.9940) than the SYS group.
Conclusions: IAC could effectively and safely decrease
postresection hepatic metastases and improve 3-year HMFS and OS of stage 2–3
GBC.
Keywords: gallbladder
cancer, intra-arterial chemotherapy, hepatic metastases, survival