109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
支架辅助血管成形术对颅内/颅外动脉狭窄患者的认知状况和血清 β 淀粉样蛋白含量的影响
Authors Zhao L, Zhao Y, Zhang H
Published Date February 2015 Volume 2015:11 Pages 471—475
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S79950
Received 28 December 2014, Accepted 29 January 2015, Published 24 February 2015
Aim: The study reported here aimed to examine how stent-assisted angioplasty
affects cognitive status and serum levels of amyloid betas (Aβs) 1-40 and 1-42
in patients with cerebral arterial stenosis.
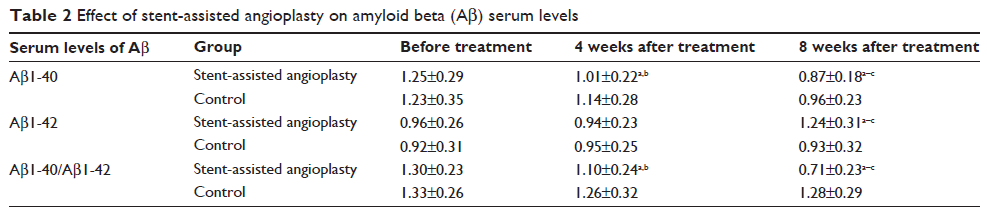
Methods: Patients with cerebral arterial stenosis were given stent-assisted angioplasty plus conventional treatment (stent-assisted angioplasty group) or conventional treatment alone (control group). Cognitive status and Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 serum levels were determined before treatment and at 4 and 8 weeks after treatment.
Results: At 4 weeks after treatment, cognitive status in patients with stent-assisted angioplasty had clearly improved. Aβ1-42 serum levels changed insignificantly in all patients. However, Aβ1-40 serum levels and Aβ1-40/Aβ1-42 ratio decreased further in patients with stent-assisted angioplasty than in patients who received conventional treatment (controls). Eight weeks after treatment, cognitive status in patients who had undergone stent-assisted angioplasty were continuing to improve, Aβ1-42 serum levels had begun to increase dramatically, and Aβ1-40 serum levels and Aβ1-40/Aβ1-42 ratio had declined further.
Conclusion: Stent-assisted angioplasty could improve cognitive status and decrease Aβ1-40 serum levels and Aβ1-40/Aβ1-42 ratio.
Keywords: arterial stenosis, Alzheimer’s disease, Aβ1-40, Aβ1-42, Aβ1-40/Aβ1-42 ratio
Methods: Patients with cerebral arterial stenosis were given stent-assisted angioplasty plus conventional treatment (stent-assisted angioplasty group) or conventional treatment alone (control group). Cognitive status and Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 serum levels were determined before treatment and at 4 and 8 weeks after treatment.
Results: At 4 weeks after treatment, cognitive status in patients with stent-assisted angioplasty had clearly improved. Aβ1-42 serum levels changed insignificantly in all patients. However, Aβ1-40 serum levels and Aβ1-40/Aβ1-42 ratio decreased further in patients with stent-assisted angioplasty than in patients who received conventional treatment (controls). Eight weeks after treatment, cognitive status in patients who had undergone stent-assisted angioplasty were continuing to improve, Aβ1-42 serum levels had begun to increase dramatically, and Aβ1-40 serum levels and Aβ1-40/Aβ1-42 ratio had declined further.
Conclusion: Stent-assisted angioplasty could improve cognitive status and decrease Aβ1-40 serum levels and Aβ1-40/Aβ1-42 ratio.
Keywords: arterial stenosis, Alzheimer’s disease, Aβ1-40, Aβ1-42, Aβ1-40/Aβ1-42 ratio