108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

三氯生治疗降低了索拉非尼在肝癌细胞中的抗肿瘤作用
Authors Wu M, Zhao G, Zhuang X, Zhang T, Zhang C, Zhang W, Zhang Z
Received 13 February 2018
Accepted for publication 19 March 2018
Published 18 May 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 2945—2954
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S165436
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
Background: Triclosan is a widely applied antimicrobial agent which affects the
endocrine system and homeostasis; it may also promote the cirrhosis and
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) growth in a mice model. The exact roles of
triclosan in regulating human hepatocellular carcinoma development and treatment
remain unknown.
Methods: MHCC97-H, a highly aggressive HCC cell line, was treated with
indicated concentration of triclosan or sorafenib. The expression of
drug-resistance genes was examined by qPCR. The clearance or metabolism of
sorafenib was determined by liquid chromatograph-mass spectrometer/mass
spectrometer (LC-MS/MS). MTT assay was used to examine the MHCC97-H cell
proliferation. Nude mice were used to exam the anti-tumor effect of sorafenib
on subcutaneous and intrahepatic growth of MHCC97-H cells.
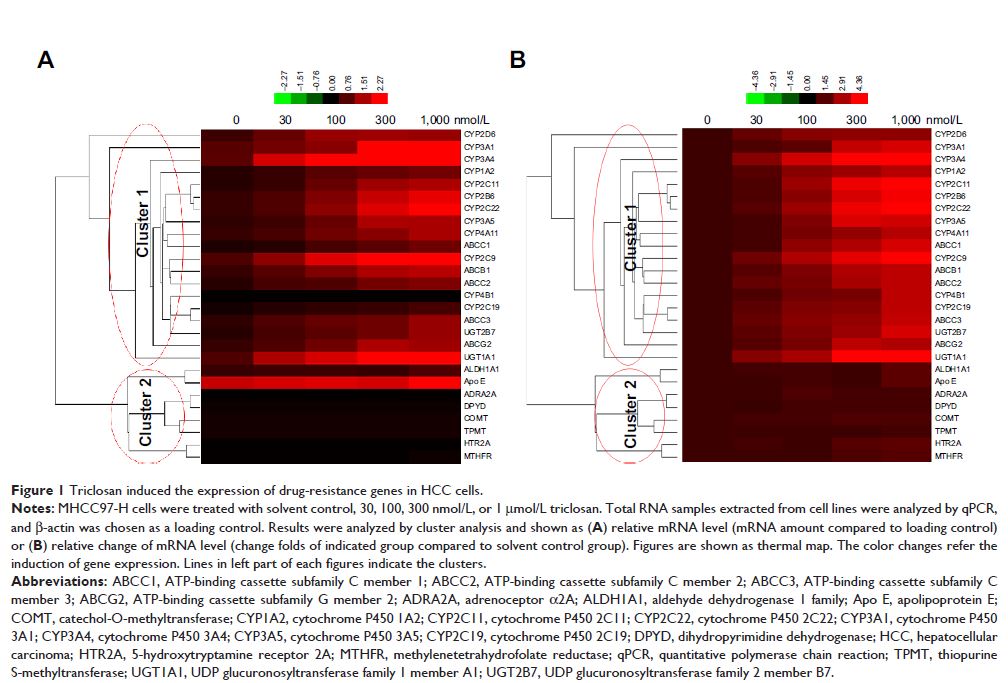
Results: In the present study, triclosan could induce the expression of
drug-resistance genes in MHCC97-H cells (a highly aggressive HCC cell line),
accelerate the clearance of sorafenib, and attenuate the anti-proliferation
effect of this molecular targeted agent in MHCC97-H cells. Triclosan decreased
the antitumor effect of sorafenib on subcutaneous and intrahepatic growth of
MHCC97-H in nude mice.
Conclusion: By discovering the fact that triclosan treatment enhances sorafenib
resistance in HCC cells, this work suggests exposure of triclosan is
detrimental to HCC patients during chemotherapy.
Keywords: HCC, triclosan, sorafenib resistance, drug clearance