108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

PDIA3 的下调抑制人急性骨髓性白血病细胞的增殖和侵袭
Authors Ye Q, Fu P, Dou J, Wang N
Received 12 January 2018
Accepted for publication 24 February 2018
Published 17 May 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 2925—2935
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S162407
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
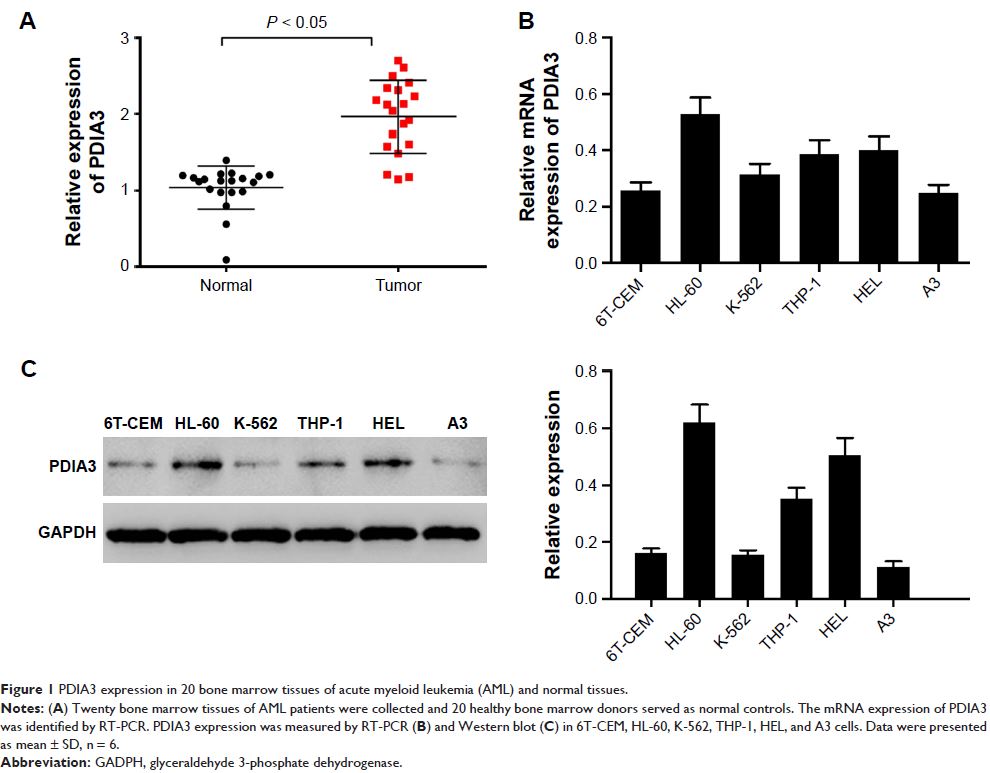
Introduction: Acute
myeloid leukemia (AML) is a common malignancy of the hematopoietic system. In
bone marrow samples of AML patients, PDIA3 expression was higher than that in
the samples of healthy controls. We aimed at exploring the effect of PDIA3
siRNA on proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion of AML HL-60 and HEL
cells.
Materials and
methods: RT-PCR was performed to identify
PDIA3 expression. Cell proliferation was assessed by MTT. Flow cytometry
analysis and transwell were used to detect cell apoptosis, migration and
invasion. Gene set enrich-ment analysis (GSEA) was employed to explore the PDIA
3-associated pathways in AML. Western blotting was used for protein expression
detection.
Results: PDIA3 siRNA significantly inhibited the proliferation of AML cells
at 24 and 48 h. PDIA3 siRNA notably enhanced the percentage of apoptotic cells.
The migration and invasion abilities of HL-60 and HEL cells in the PDIA3 siRNA
group were significantly suppressed compared with those in the control and siNC
groups. GSEA of the Cancer Genome Atlas dataset showed that Kyoto Encyclopedia
of Genes and Genomes oxidative phosphorylation and amino sugar and nucleotide
sugar metabolism pathways could be correlated with PDIA3 expression; this was
further confirmed in AML cells by Western blotting. MAPK signaling was also
blocked by PDIA3 siRNA.
Conclusion: PDIA3 siRNA effectively enhanced apoptosis, and suppressed
proliferation, invasion, and migration of AML cells by regulating oxidative
phosphorylation and amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism pathways, and
MAPK signaling, which can provide novel therapeutic targets for AML.
Keywords: PDIA3, acute myeloid leukemia, migration, invasion, gene set
enrichment analysis, MAPK pathway