108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

二氯乙酸通过抑制非小细胞肺癌中的自噬增强了化疗药物的抗肿瘤功效
Authors Lu X, Zhou D, Hou B, Liu QX, Chen Q, Deng XF, Yu ZB, Dai JG, Zheng H
Received 9 November 2017
Accepted for publication 3 March 2018
Published 16 May 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 1231—1241
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S156530
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background: Chemotherapy is still the primary adjuvant strategy of cancer
therapy; however, the emergence of multi-drug resistance has been a cause for
concern. Autophagy has been demonstrated to have a protective role against
chemotherapeutic drugs in cancer cells, and autophagy inhibition is generally
considered to be a promising therapeutic strategy. However, the paucity of
effective and specific autophagy inhibitors limits its application.
Purpose: The objective of this study was to explore the
effect of DCA, small molecular antitumor agent, on the autophagy regulation and
chemosensitization in NSCLC cells.
Methods: We investigated the autophagy regulation of
dichloroacetate (DCA) by laser confocal microscopy and western blotting in A549
and H1975 cell lines. The MTT assay and flow cytometry was performed for
explore the chemosensitization effectiveness of DCA. The results were verified
with subcutaneous tumor model in nude mice and the immunohistochemistry was
applied for assessing the level of cell apoptosis and autophagy in vivo post
treatment.
Results: We found that DCA, which exhibited antitumor
properties in various carcinoma models, induced apoptosis of non-small cell
lung cancer cells (NSCLC) by inhibiting cancer cell autophagy. Furthermore,
Perifosine, an AKT inhibitor, can greatly weaken the capacity of inducing
apoptosis by DCA. The results indicate that the AKT-mTOR pathway, a main
negative regulator of autophagy, is involved in the DCA-induced inhibition of
autophagy. Then, we detected the effectiveness of autophagy inhibition by DCA.
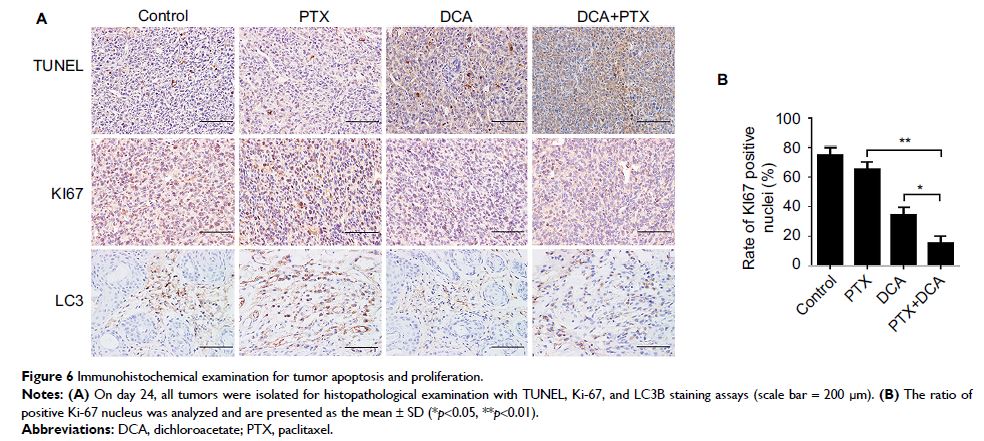
When used in co-treatment with the chemotherapeutic drug paclitaxel (PTX), DCA
markedly decreased cell autophagy, enhanced apoptosis and inhibited
proliferation in A549 and H1975 cells. The results of the xenograft experiment
demonstrate that co-treatment of PTX and DCA can significantly decrease cell
proliferation in vivo and prolong the survival of mice.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that DCA can inhibit cell
autophagy induced by chemotherapeutics, providing a new avenue for cancer
chemotherapy sensitization.
Keywords: DCA, autophagy,
multi-drug resistance, non-small-cell lung cancer, paclitaxel, xenograft nude
mice, chemosensitization