108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

WWC3 通过激活 Hippo-YAP 信号传导来抑制肺癌的上皮-间质转化
Authors Han Q, Kremerskothen J, Lin X, Zhang X, Rong X, Zhang D, Wang E
Received 12 January 2018
Accepted for publication 2 March 2018
Published 8 May 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 2581—2591
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S162387
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tohru Yamada
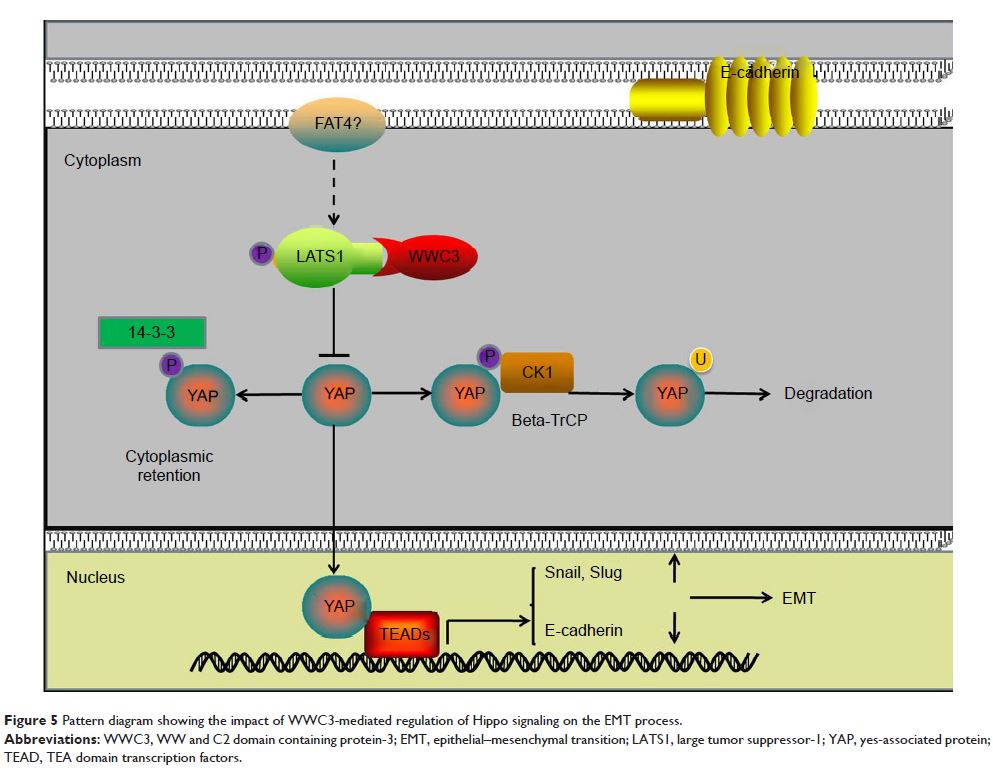
Background: Though we recently reported that the WWC3 inhibits the
invasiveness and metastasis of lung cancer by activating the Hippo pathway, the
impact and underlying mechanisms of this process still remain unclear.
Methods: To identify the role of WWC3 in epithelial-mesenchymal transition
of lung cancer, we performed immunohistochemistry to detect the expression
levels of WWC3 and EMT-related biomarker, and analyzed their correlations in a
cohort of 127 patients with NSCLC. Wound healing assay and cell invasion assay
were applied to explore cell invasive ability change after WWC3 knockdown.
qRT-PCR and immunoblotting were performed to assess mRNA and protein levels of
EMT-related biomarkers and the main molecules changes of Hippo signaling caused
by WWC3. Immunoprecipition was to examine WWC3 and LATS1 interaction.
Results: WWC3 knockdown drives a pronounced shift from the epithelial to
the mesenchymal phenotype in lung cancer cells. In addition, WWC3 ectopic
expression in lung cancer cells attenuates mesenchymal markers and increases
the epithelial markers expressions; however, WWC3-ΔWW plasmid abrogated these
effects. WWC3 silencing by shRNA exerts the opposite effect. Furthermore, WWC3
levels were inversely correlated with the levels of EMT inducers (Snail and
Slug) in lung cancer cells and specimens. Immunoblotting revealed that WWC3
wild-type upregulates large tumor suppressor (LATS1) and yes-associated protein
(YAP) phosphorylation through its WW domain, hence activating Hippo pathway.
Knockdown of YAP and LATS1, as well as the as the Verteporfin (VP) usage, could
reverse this effect caused by WWC3 silencing.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that WWC3 works as a tumor suppressor to
inhibit EMT process and confer its candidacy as a potential therapeutic target
in lung cancer.
Keywords: WWC3, epithelial–mesenchymal transition, Hippo pathway, YAP,
nonsmall-cell lung cancer