109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

D-α-生育酚聚乙二醇 1000 琥珀酸盐-b-poly(ε-己内酯-ran-乙交酯)双嵌段共聚物的纳米制剂作为小干扰 RNA,用于鼻咽癌治疗
Authors Chen Y, Xu G, Zheng Y, Yan M, Li Z, Zhou Y, Mei L, Li X
Published Date February 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 1375—1386
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S76092
Received 20 October 2014, Accepted 12 January 2015, Published 17 February 2015
Abstract: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) is a crucial transcription factor that
plays an important role in the carcinogenesis and development of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. In this research, a novel biodegradable D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene
glycol 1000 succinate-b-poly(ε-caprolactone-ran-glycolide)
(TPGS-b-(PCL-ran-PGA)) nanoparticle (NP) was prepared as a delivery system for
small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) molecules targeting HIF-1α in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma gene therapy. The results showed that the NPs could efficiently
deliver siRNA into CNE-2 cells. CNE-2 cells treated with the HIF-1α
siRNA-loaded TPGS-b-(PCL-ran-PGA) NPs showed reduction of HIF-1α expression
after 48 hours of incubation via real-time reverse
transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and Western blot analysis. The
cytotoxic effect on CNE-2 cells was significantly increased by HIF-1α
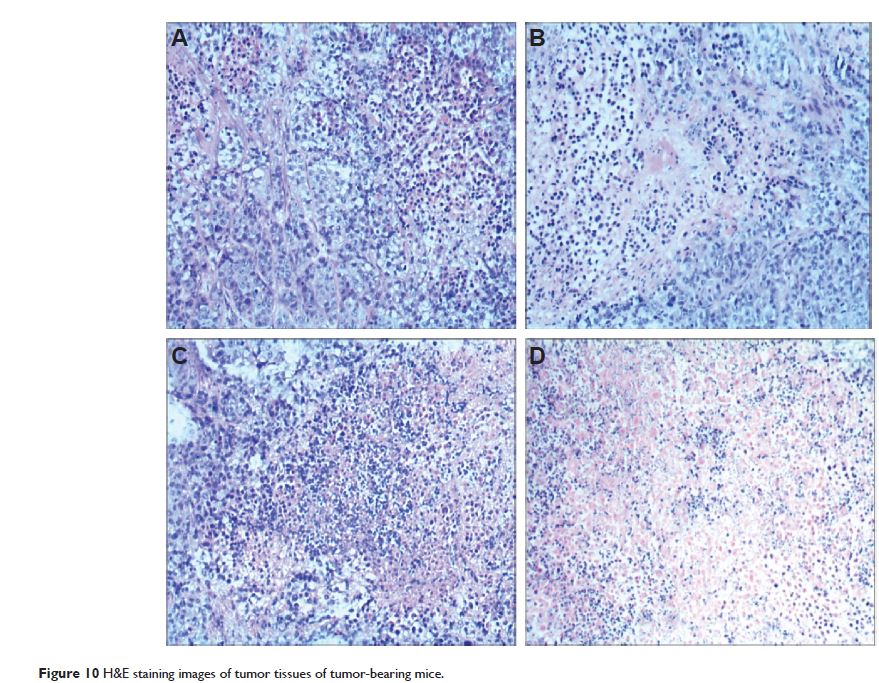
siRNA-loaded NPs when compared with control groups. In a mouse tumor xenograft
model, the HIF-1α siRNA-loaded NPs efficiently suppressed tumor growth, and the
levels of HIF-1α mRNA and protein were significantly decreased. These results
suggest that TPGS-b-(PCL-ran-PGA) NPs could function as a promising genetic
material carrier in antitumor therapy, including therapy for nasopharyngeal
carcinoma.
Keywords: TPGS-b-(PCL-ran-PGA),
nanoparticles, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, gene
delivery