108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

五味子乙素通过抑制 NF-κB 和 MAPK 信号通路改善软骨细胞炎症和骨关节炎
Authors Ran J, Ma C, Xu K, Xu L, He Y, Moqbel SAA, Hu P, Jiang L, Chen W, Bao J, Xiong Y, Wu L
Received 9 January 2018
Accepted for publication 28 February 2018
Published 9 May 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 1195—1204
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S162014
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Palas Chanda
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Introduction: Osteoarthritis
(OA) is the most prevalent joint disorder in the elderly population, and
inflammatory mediators like IL-1βwere thought to play central roles in its
development. Schisandrin B, the main active component derived from Schisandra chinensis , exhibited
antioxidative and antiinflammatory properties.
Methods: In the present study, the protective effect and the underlying
mechanism of Schisandrin B on OA was investigated in vivo and in vitro.
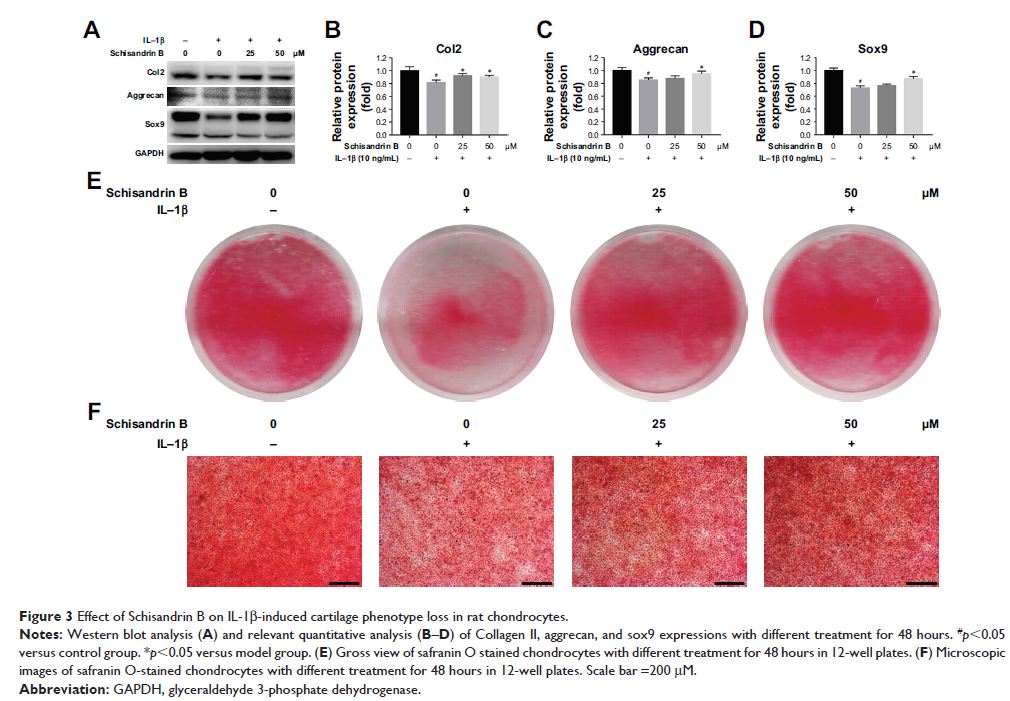
Results: The results showed that Schisandrin B decreased IL-1β-induced
upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase 3 (MMP3), MMP13, IL-6, and inducible
nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and increased IL-1β-induced downregulation of
collagen II, aggrecan, and sox9 as well. Schisandrin B significantly decreased
IL-1β-induced p65 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of p65 in rat
chondrocytes. Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation was also
inhibited by Schisandrin B, as evidenced by the reduction of p38, extracellular
signal-regulated kinase (Erk), and c-Jun amino-terminal kinase (Jnk)
phosphorylation. In addition, Schisandrin B prevented cartilage degeneration in
rat OA model with significantly lower Mankin’s score than the control
group.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that Schisandrin B ameliorated chondrocytes
inflammation and OA via suppression of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and MAPK
signal pathways, indicating a therapeutic potential in OA treatment.
Keywords: osteoarthritis, Schisandrin B, chondrocytes, MMPs, NF-κB pathway,
MAPK pathway