108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

由溶剂前沿突变 G1202R 引起的间变性淋巴瘤激酶对 alectinib 和 JH-VIII-157-02 耐药机制的认识
Authors Wang H, Wang Y, Guo W, Du B, Huang X, Wu R, Yang B, Lin X, Wu Y
Received 24 July 2017
Accepted for publication 19 December 2017
Published 9 May 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 1183—1193
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S147104
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Background: Mutated anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) drives the development of
advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Most reported small-molecule
inhibitors targeting the ALK domain do not display good inhibition of the
G1202R solvent front mutation. The solvent front mutation was assumed to hinder
drug binding. However, a different fact could be uncovered by the simulations
reported in this study through a structural analog of alectinib
(JH-VIII-157-02), which demonstrated potent effects against the G1202R
mutation.
Methods: Molecular docking, conventional molecular dynamics (MD)
simulations, free energy calculations, and umbrella sampling (US) simulations
were carried out to make clear the principles of the binding preferences of
alectinib and JH-VIII-157-02 toward ALKWT and the ALK G1202R (ALKG1202R) mutation.
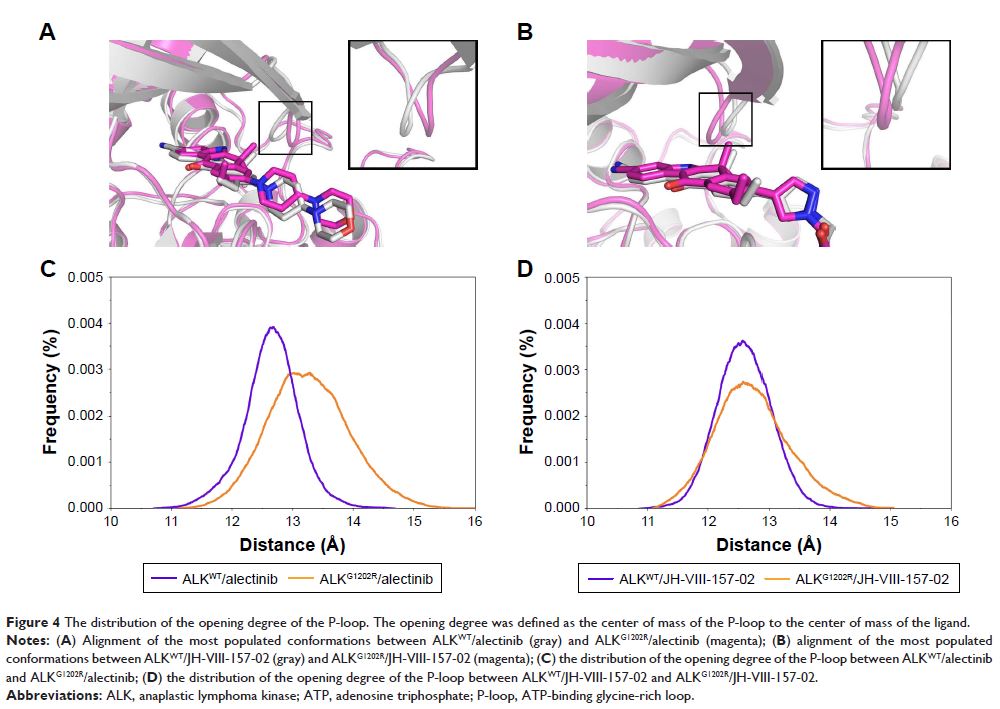
Results: JH-VIII-157-02 has similar binding affinities to both ALKWT and ALKG1202R whereas it has has a much lower binding affinity for alectinib to
ALKG1202R.
Analysis of individual energy terms indicate the major variation involves the
van der Waals and entropy terms. Structural analysis reveals that the
conformational change of the ATP-binding glycine-rich loop was primarily responsible
for the alectinib resistance, not JH-VIII-157-02. In addition, US simulations
prove JH-VIII-157-02 has similar dissociative processes from both ALKWT and ALKG1202R, while alectinib is more easily dissociated from ALKG1202R than from ALKWT, thus indicating lesser residence time.
Conclusion: Both the binding affinity and the drug residence time should be
emphasized in rational drug design to overcome the G1202R solvent front
mutation in ALK resistance.
Keywords: ALK, G1202R, alectinib, JH-VIII-157-02, theoretical study,
resistance mechanisms