108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在中国一个由医师和药剂师联合管理的诊所评估患者的华法林知识和抗凝控制
Authors Li X, Sun S, Wang Q, Chen B, Zhao Z, Xu X
Received 10 November 2017
Accepted for publication 1 March 2018
Published 9 May 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 783—791
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S156734
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Naifeng Liu
Purpose: Warfarin is a widely used anticoagulant with a narrow therapeutic
index, and it requires close monitoring and adequate patient education. We
aimed to assess the knowledge level regarding warfarin therapy among its users and
to identify the factors that significantly influence anticoagulation control.
Patients and
methods: Patients attending the
Warfarin Clinic at the Beijing Tiantan Hospital were enrolled in this study.
Patients’ knowledge on warfarin was assessed using a validated Anticoagulation
Knowledge Assessment (AKA) questionnaire. Patients’ responses to each question
were analyzed to identify areas of improvement in current warfarin education.
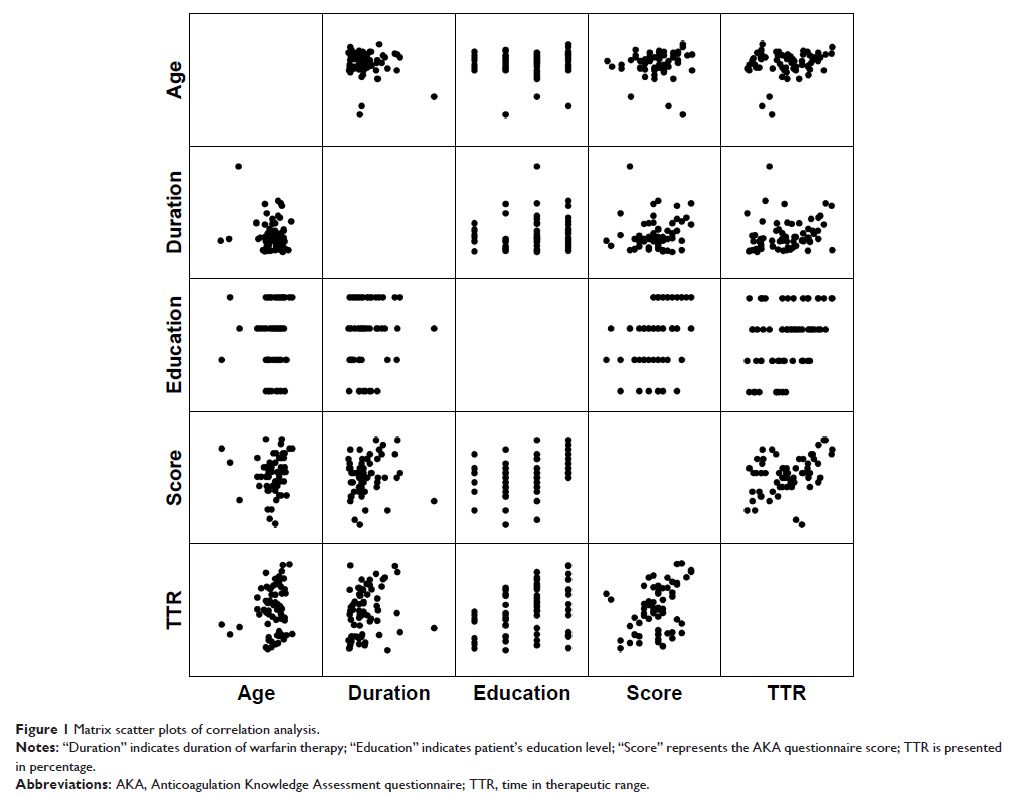
International normalized ratio (INR) control was defined by the time in therapeutic
range (TTR) calculated using the Rosendaal method. Spearman correlation
analysis was used to investigate the association between TTR and the
independent variables.
Results: A total of 65 patients were enrolled in this study. Eleven questions were
answered correctly by <50% of the patients. A total of 858 INR results were
recorded; 432 INR values (50.3%) reached the predefined goals, and the mean TTR
was 49.8%±24.8%. There were significant associations between TTR and patients’
AKA scores (R =0.356, P =0.004) and between TTR and
patients’ educational levels (R =0.339, P =0.006). No significant
association was observed between other factors (age and duration of
anticoagulation) and TTR. The INR outcome measure was positively associated
with patients’ knowledge on warfarin and their educational levels.
Conclusion: Areas for improvement in patient education have been identified, and
processes for educational modification are currently in development.
Keywords: International normalized ratio, educational level, People’s
Republic of China