108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

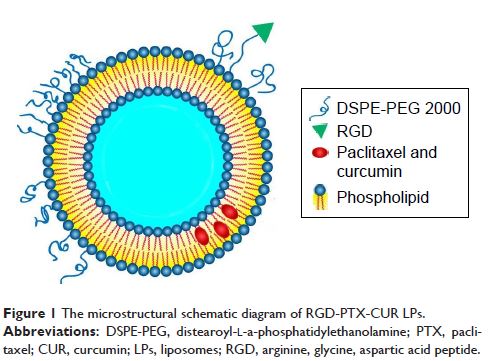
精氨酸、甘氨酸、天冬氨酸肽修饰的紫杉醇和姜黄素共负载脂质体用于治疗肺癌:体外/体内评估
Authors Jiang K, Shen M, Xu W
Received 22 November 2017
Accepted for publication 16 March 2018
Published 27 April 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 2561—2569
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S157746
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Purpose: In
this study, a novel arginine, glycine, aspartic acid peptide (RGD)-modified
paclitaxel and curcumin co-loaded liposomes were developed to evaluate their
antitumor activity in vitro and in vivo.
Materials and
methods: Co-loaded liposomes were prepared
using the solvent evaporation method. The particles had spherical shapes under
electron microscopy with sizes <130 nm.
Results: By comparison with the free drug, RGD-modified paclitaxel and
curcumin co-loaded liposomes and paclitaxel and curcumin co-loaded liposomes
have sustained-release properties in vitro. In vivo, there was no significant
difference in pharmacokinetic parameters between the RGD-modified paclitaxel
and curcumin co-loaded liposomes and paclitaxel and curcumin co-loaded
liposomes. A strong green fluorescence was observed in the cytoplasmic region
after incubation of RGD-modified paclitaxel and curcumin co-loaded liposomes
for 2 h. RGD-modified paclitaxel and curcumin co-loaded liposomes showed a
superior antiproliferative effect on A549 cells with a possible mechanism that
suppressed the multidrug resistance phenomenon and exhibited a clear synergistic
effect.
Conclusion: The results indicate that RGD-modified paclitaxel and curcumin
co-loaded liposomes had a better antitumor effect in vivo than the non-modified
LPs. These results indicate that RGD-modified co-loaded liposomes are a
promising candidate for antitumor drug delivery.
Keywords: arginine, glycine, aspartic acid peptide, paclitaxel, curcumin,
liposome, cell uptake, cytotoxicity study, in vivo anti-tumor study