108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长链非编码 RNA MALAT1 与癌胚抗原相结合用于诊断肺癌恶性胸腔积液
Authors Wang WW, Zhou XL, Song YJ, Yu CH, Zhu WG, Tong YS
Received 20 November 2017
Accepted for publication 10 February 2018
Published 24 April 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 2333—2344
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S157551
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Purpose: Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are present in body fluids, but their
potential as tumor biomarkers has never been investigated in malignant pleural
effusion (MPE) caused by lung cancer. The aim of this study was to assess the
clinical significance of lncRNAs in pleural effusion, which could potentially
serve as diagnostic and predictive markers for lung cancer-associated MPE
(LC-MPE).
Patients and methods: RNAs from pleural effusion were extracted in 217
cases of LC-MPE and 132 cases of benign pleural effusion (BPE). Thirty-one lung
cancer-associated lncRNAs were measured using quantitative real-time polymerase
chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The level of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) was also
determined. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and the area
under the ROC curve (AUC) were established to evaluate the sensitivity and
specificity of the identified lncRNAs and other biomarkers. The correlations
between baseline pleural effusion lncRNAs expression and response to
chemotherapy were also analyzed.
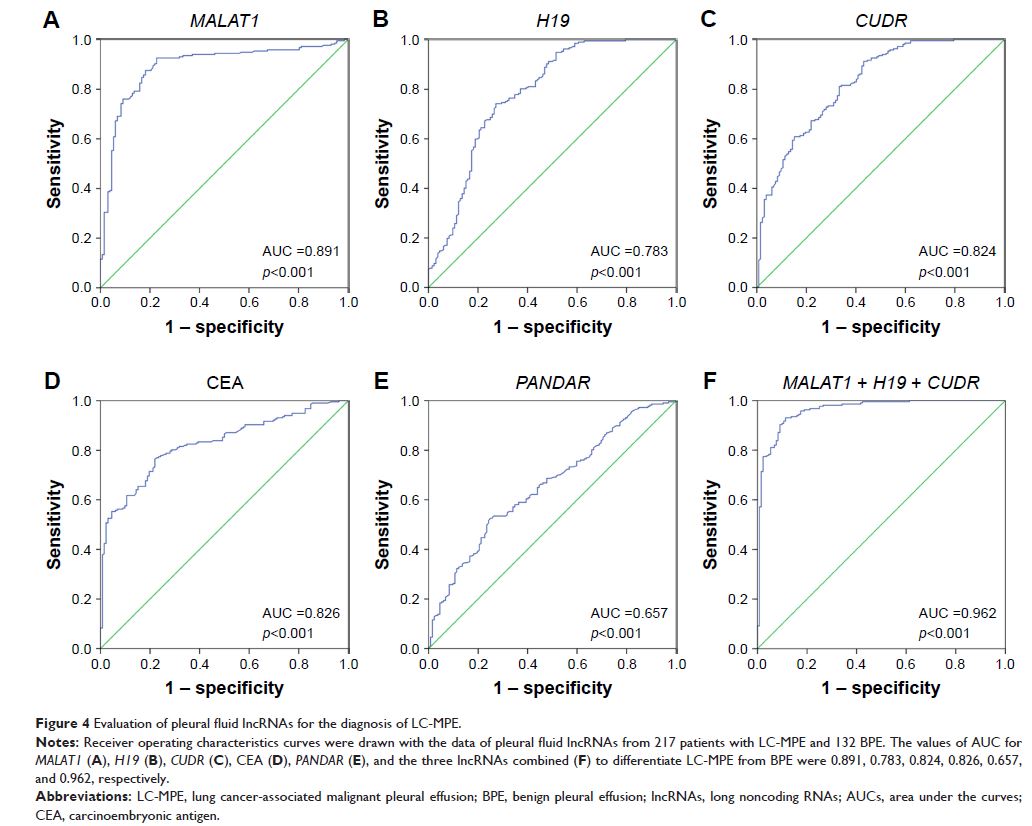
Results: Three lncRNAs (MALAT1 , H19 , and CUDR ) were found to have potential
as diagnostic markers in LC-MPE. The AUCs for MALAT1 , H19 , CUDR , and CEA were 0.891, 0.783,
0.824, and 0.826, respectively. Using a logistic model, the combination
of MALAT1 and CEA (AUC, 0.924)
provided higher sensitivity and accuracy in predicting LC-MPE than CEA (AUC,
0.826) alone. Moreover, baseline MALAT1 expression
in pleural fluid was inversely correlated with chemotherapy response in
patients with LC-MPE.
Conclusion: Pleural effusion lncRNAs were effective in
differentiating LC-MPE from BPE. The combination of MALAT1 and
CEA was more effective for LC-MPE diagnosis.
Keywords: malignant
pleural effusion, lncRNA, MALAT1 , lung cancer,
diagnosis